Product Description
Fundamental contents
High-pressure water pump, the most widely used should be the miniature high-pressure water pump. Because it has the characteristics of high pressure, small size, easy to carry, and can be driven by a car battery, it is often used for cleaning, spraying, spraying, and pressurizing.
Characteristics and parameters of high-pressure water pumps
micro water pump, micro high pressure water pump, 24V high pressure water pump
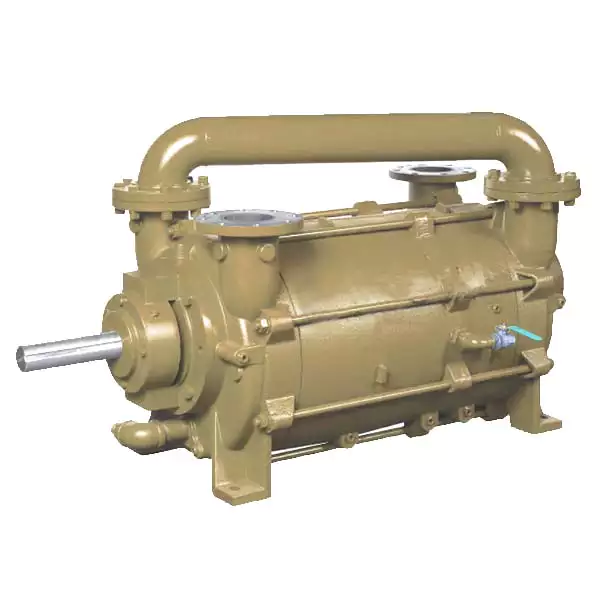
Mini high-pressure water pump (Xinweicheng brand)-self-priming, ultra-high pressure, small size (HSP series)
Model: HSP11050 (Xinweicheng)
Pressure: 11 kg
Flow rate: 7L/Min
Its main features are: 1. Ultra-high pressure (11kg MAX), large flow (7L/MIN), high suction (1m), low noise; stable self-priming function, no need to add “water diversion” first, self The suction speed is extremely fast.
Overpressure, overheating double automatic protection switch, automatic shutdown protection when the output pressure exceeds the maximum pressure; automatic protection when the temperature is too high. Two kinds of interfaces can be connected to soft and hard pipes respectively, equipped with metal joints, which are not easy to damage.
Integrating the advantages of self-priming pumps and chemical pumps, it is synthesized with a variety of corrosion-resistant imported materials, and has the properties of acid resistance, alkali resistance, and corrosion resistance. The pump body is separated from the motor, and the working medium does not contact the motor. There are no mechanical parts in the pump body, and there is no mechanical wear.
It runs smoothly, can be idling, and has an extremely long service life.
exquisite workmanship, small size, light weight, stable performance, easy installation;
Mini high-pressure water pump use
can pump water, liquid (solution), pressurize the water outlet (maximum pressure is up to 11 kg), suitable for liquid spraying, spraying, washing, irrigation, showering, transfer, lifting, cleaning and many other occasions.
Application range of micro high pressure water pump
customers in many fields such as water treatment, liquid sampling, scientific research, instrumentation, chemical analysis, healthcare, medicine and hygiene, bioengineering, automatic control, environmental protection, etc.
Selection guide for miniature water pumps:
1. Large flow requirements (about 4-20 liters/minute), low pressure requirements (about 1-3 kg), mainly used for water circulation, water sampling, lifting, etc., requiring low noise, long life, and high self-priming Process, etc., BSP, CSP, etc. series can be selected;
2. The flow rate is not high (about 1 to 5 liters/minute), but the pressure is relatively high (about 2 to 11 kg), it is mainly used for spraying, pressurizing, car washing, etc. It does not need to work for a long time under high pressure or heavy load. , You can choose ASP, HSP, etc. series;
3. Used for tea table pumping, spraying, etc., the volume is as small as possible, the flow rate is small, and the noise is low (about 0.1 to 3 liters/min), and ASP series are optional.
Fourth, high-temperature working medium (0-100 ºC), need to pump water or gas (may be water-gas mixture or idling, dry running occasions), value volume, noise, continuous use and other performance. The pump needs to run idling and dry for a long time. If there is both water and gas in the pipeline, you need to choose the WKA series of water and gas dual-purpose pumps. The WKA series of miniature water pumps are especially suitable for occasions where water and air are present. For the above applications, WKA series can be selected.
5. There is a large requirement for the flow rate (more than 20 liters/min), but the medium contains a small amount of oil, CHINAMFG particles, residues, etc.
Three series of micro submersible pumps, QZ (medium flow rate 35-45 liters/minute), QD (large flow rate 85-95 liters/minute), QC (super large flow rate 135-145 liters/minute), and DC submersible pumps can be selected Pump.
SERVICE
We have established some overseas agent office to make the after-sales serivce already ,so it can will be service client in fast response .also in our headquarter service team ,there is a expert team which can support client in 7*24 hours .
1. Customer inquiry and consultation (URS documents)
2. Confirmation of treatment plan (DQ documents &PID Drawing)
3.Quotation offer with the technolgy document (Quotation PI )
4.Engineering and Manufacturing (Prodcution &Quality inspection )
5. Product inspection (FAT documents)
6. Delivery arrangement and loading work (full set Shipment documents)
7. After-sales service (OQ,PQ ,SAT documents)
FAQ
1.What about your factory?
Our factory is located in HangZhou city ,ZHangZhoug Province and have more than 15 years experience on machinery making.
2.How will your company control the equipment quality ?
We have a qualified expert team ,we will inspect every production proceed .also Machines will be tested in our plant before shipment .
3.How long the warranty will be?
We provide 1 years warranty for the machine running ,but we will afford whole -life service for the machine .
4.Which kind payment do your company do now ?
We accept Western Union, T/T ,D/P,D/C and irrevocable L/C payable etc.
5.Can we become your distributor in our country?
Yes, we very welcome you! More details will be discussed if you are interested in being our agent.
6.Why we choose “JOSTON “?
1. We enhance the reliability of product’s quality and working life .
2. We decrease the consumption cost of the product in the ruuning.
3. We improve research personnel’s ability to deliver a creative design;
4. We use leading technologies in our product development and innovation, and thereby increase the competitive advantage of products.
7.Do you supply installation equipment in oversea?
Yes, if need, we can send our engineer to your plant to help you do installation and commission.
8.How can we know the order production status ?
We will arrange the person to take photo or video during manufacturing in every week to make you to know the production status.When goods are finished,we will take detailed photos or video for your checking ,after approve ,then we will arrange shipment .also you can arrange FAT in our plant when the goods is ready here
9.what is kind service do you offer before making order ?
1.according to your company URS ,we will make the design drawing accoridingly.
2.after your company approved drawing ,we will make quotation.
3. final we make agreement on payment terms ,delivery time ,package ,shipment etc.
10.how about your company after-sale serivce ?
1. We provide long-term after-sale service.
2. we can do installation and commission for the equipment in your plant if necessary .
3. Meanwhile, you can call or e-mail us to consult on any relevant question since we have a special line for after-sale service. Alternatively, you can communicate on-line with us to solve any problem.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online Support/Visit Client′s Plant Site |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Max.Head: | Customized |
| Max.Capacity: | Customized |
| Driving Type: | Motor |
| Material: | 304/316L Stainless Steel |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Is the Impact of Altitude on Vacuum Pump Performance?
The performance of vacuum pumps can be influenced by the altitude at which they are operated. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Altitude refers to the elevation or height above sea level. As the altitude increases, the atmospheric pressure decreases. This decrease in atmospheric pressure can have several effects on the performance of vacuum pumps:
1. Reduced Suction Capacity: Vacuum pumps rely on the pressure differential between the suction side and the discharge side to create a vacuum. At higher altitudes, where the atmospheric pressure is lower, the pressure differential available for the pump to work against is reduced. This can result in a decrease in the suction capacity of the vacuum pump, meaning it may not be able to achieve the same level of vacuum as it would at lower altitudes.
2. Lower Ultimate Vacuum Level: The ultimate vacuum level, which represents the lowest pressure that a vacuum pump can achieve, is also affected by altitude. As the atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude, the ultimate vacuum level that can be attained by a vacuum pump is limited. The pump may struggle to reach the same level of vacuum as it would at sea level or lower altitudes.
3. Pumping Speed: Pumping speed is a measure of how quickly a vacuum pump can remove gases from a system. At higher altitudes, the reduced atmospheric pressure can lead to a decrease in pumping speed. This means that the vacuum pump may take longer to evacuate a chamber or system to the desired vacuum level.
4. Increased Power Consumption: To compensate for the decreased pressure differential and achieve the desired vacuum level, a vacuum pump operating at higher altitudes may require higher power consumption. The pump needs to work harder to overcome the lower atmospheric pressure and maintain the necessary suction capacity. This increased power consumption can impact energy efficiency and operating costs.
5. Efficiency and Performance Variations: Different types of vacuum pumps may exhibit varying degrees of sensitivity to altitude. Oil-sealed rotary vane pumps, for example, may experience more significant performance variations compared to dry pumps or other pump technologies. The design and operating principles of the vacuum pump can influence its ability to maintain performance at higher altitudes.
It’s important to note that vacuum pump manufacturers typically provide specifications and performance curves for their pumps based on standardized conditions, often at or near sea level. When operating a vacuum pump at higher altitudes, it is advisable to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and consider any altitude-related limitations or adjustments that may be necessary.
In summary, the altitude at which a vacuum pump operates can have an impact on its performance. The reduced atmospheric pressure at higher altitudes can result in decreased suction capacity, lower ultimate vacuum levels, reduced pumping speed, and potentially increased power consumption. Understanding these effects is crucial for selecting and operating vacuum pumps effectively in different altitude environments.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in the Production of Solar Panels?
Yes, vacuum pumps are extensively used in the production of solar panels. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. The manufacturing process of solar panels involves several critical steps, many of which require the use of vacuum pumps. Vacuum technology plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency, reliability, and quality of solar panel production. Here are some key areas where vacuum pumps are utilized:
1. Silicon Ingot Production: The first step in solar panel manufacturing is the production of silicon ingots. These ingots are cylindrical blocks of pure crystalline silicon that serve as the raw material for solar cells. Vacuum pumps are used in the Czochralski process, which involves melting polycrystalline silicon in a quartz crucible and then slowly pulling a single crystal ingot from the molten silicon. Vacuum pumps create a controlled environment by removing impurities and preventing contamination during the crystal growth process.
2. Wafering: After the silicon ingots are produced, they undergo wafering, where the ingots are sliced into thin wafers. Vacuum pumps are used in wire saws to create a low-pressure environment that helps to cool and lubricate the cutting wire. The vacuum also assists in removing the silicon debris generated during the slicing process, ensuring clean and precise cuts.
3. Solar Cell Production: Vacuum pumps play a significant role in various stages of solar cell production. Solar cells are the individual units within a solar panel that convert sunlight into electricity. Vacuum pumps are used in the following processes:
– Diffusion: In the diffusion process, dopants such as phosphorus or boron are introduced into the silicon wafer to create the desired electrical properties. Vacuum pumps are utilized in the diffusion furnace to create a controlled atmosphere for the diffusion process and remove any impurities or gases that may affect the quality of the solar cell.
– Deposition: Thin films of materials such as anti-reflective coatings, passivation layers, and electrode materials are deposited onto the silicon wafer. Vacuum pumps are used in various deposition techniques like physical vapor deposition (PVD) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to create the necessary vacuum conditions for precise and uniform film deposition.
– Etching: Etching processes are employed to create the desired surface textures on the solar cell, which enhance light trapping and improve efficiency. Vacuum pumps are used in plasma etching or wet etching techniques to remove unwanted material or create specific surface structures on the solar cell.
4. Encapsulation: After the solar cells are produced, they are encapsulated to protect them from environmental factors such as moisture and mechanical stress. Vacuum pumps are used in the encapsulation process to create a vacuum environment, ensuring the removal of air and moisture from the encapsulation materials. This helps to achieve proper bonding and prevents the formation of bubbles or voids, which could degrade the performance and longevity of the solar panel.
5. Testing and Quality Control: Vacuum pumps are also utilized in testing and quality control processes during solar panel production. For example, vacuum systems can be used for leak testing to ensure the integrity of the encapsulation and to detect any potential defects or leaks in the panel assembly. Vacuum-based measurement techniques may also be employed for assessing the electrical characteristics and efficiency of the solar cells or panels.
In summary, vacuum pumps are integral to the production of solar panels. They are used in various stages of the manufacturing process, including silicon ingot production, wafering, solar cell production (diffusion, deposition, and etching), encapsulation, and testing. Vacuum technology enables precise control, contamination prevention, and efficient processing, contributing to the production of high-quality and reliable solar panels.
Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in the Medical Field?
Yes, vacuum pumps have a wide range of applications in the medical field. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various medical applications, providing suction or creating controlled vacuum environments. Here are some key areas where vacuum pumps are used in the medical field:
1. Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT):
Vacuum pumps are extensively utilized in negative pressure wound therapy, a technique used to promote wound healing. In NPWT, a vacuum pump creates a controlled low-pressure environment within a wound dressing, facilitating the removal of excess fluid, promoting blood flow, and accelerating the healing process.
2. Surgical Suction:
Vacuum pumps are an integral part of surgical suction systems. They provide the necessary suction force to remove fluids, gases, or debris from the surgical site during procedures. Surgical suction helps maintain a clear field of view for surgeons, enhances tissue visualization, and contributes to a sterile operating environment.
3. Anesthesia:
In anesthesia machines, vacuum pumps are used to create suction for various purposes:
– Airway Suction: Vacuum pumps assist in airway suctioning to clear secretions or obstructions from the patient’s airway during anesthesia or emergency situations.
– Evacuation of Gases: Vacuum pumps aid in removing exhaled gases from the patient’s breathing circuit, ensuring the delivery of fresh gas mixtures and maintaining appropriate anesthesia levels.
4. Laboratory Equipment:
Vacuum pumps are essential components in various medical laboratory equipment:
– Vacuum Ovens: Vacuum pumps are used in vacuum drying ovens, which are utilized for controlled drying or heat treatment of sensitive materials, samples, or laboratory glassware.
– Centrifugal Concentrators: Vacuum pumps are employed in centrifugal concentrators to facilitate the concentration or dehydration of biological samples, such as DNA, proteins, or viruses.
– Freeze Dryers: Vacuum pumps play a vital role in freeze-drying processes, where samples are frozen and then subjected to vacuum conditions to remove water via sublimation, preserving the sample’s structure and integrity.
5. Medical Suction Devices:
Vacuum pumps are utilized in standalone medical suction devices, commonly found in hospitals, clinics, and emergency settings. These devices create suction required for various medical procedures, including:
– Suctioning of Respiratory Secretions: Vacuum pumps assist in removing respiratory secretions or excess fluids from the airways of patients who have difficulty coughing or clearing their airways effectively.
– Thoracic Drainage: Vacuum pumps are used in chest drainage systems to evacuate air or fluid from the pleural cavity, helping in the treatment of conditions such as pneumothorax or pleural effusion.
– Obstetrics and Gynecology: Vacuum pumps are employed in devices used for vacuum-assisted deliveries, such as vacuum extractors, to aid in the safe delivery of babies during childbirth.
6. Blood Collection and Processing:
Vacuum pumps are utilized in blood collection systems and blood processing equipment:
– Blood Collection Tubes: Vacuum pumps are responsible for creating the vacuum inside blood collection tubes, facilitating the collection of blood samples for diagnostic testing.
– Blood Separation and Centrifugation: In blood processing equipment, vacuum pumps assist in the separation of blood components, such as red blood cells, plasma, and platelets, for various medical procedures and treatments.
7. Medical Imaging:
Vacuum pumps are used in certain medical imaging techniques:
– Electron Microscopy: Electron microscopes, including scanning electron microscopes and transmission electron microscopes, require a vacuum environment for high-resolution imaging. Vacuum pumps are employed to maintain the necessary vacuum conditions within the microscope chambers.
These are just a few examples of the wide-ranging applications of vacuum pumps in the medical field. Their ability to create suction and controlled vacuum environments makes them indispensable in medical procedures, wound healing, laboratory processes, anesthesia, and various other medical applications.


editor by Dream 2024-05-07
China manufacturer Wholesale Xgb-120 Copper Motor Machine 220V Peripheral Vacuum Pump for Agriculture and Restaurant vacuum pump for ac
Product Description
Wholesale XGB-120 Copper Motor Machine 220V Peripheral Vacuum Pump For Agriculture And Restaurant
Our Services
· Customizing the fans according to customers’ requirements.
· Delivery time for sample order: 1-5 days, for pallets order 7-20 days after receiving clear payment
· Warranty: 1 year for repairing or replacement of fans, customs duty & freight not included
FAQ
Q: How To Order ?
A: Step 1, please tell us what model and quantity you need;
Step 2, then we will make a PI for you to confirm the order details;
Step 3, when we confirmed everything, can arrange the payment;
Step 4, finally we deliver the goods within the stipulated time.
Q: What is the MOQ?
R: 100 pieces, accept sample.
Q: When you ship my order
R: Normally container need 15-40days, sample 3-7DAYS
Q: How about the quality guarantee period?
R: One year.
Q: Do you have the certificates?
R: Yes, we have passed the CE and CCC certification.
Q: Do you offer ODM & OEM service.
R: Yes, we can custom design for specific application.
Q: When can I get the quotation?
R:We usually quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry. If you are urgent to get the price, please send the message on trade management or call us directly.
Q: How can I get a sample to check your quality?
R:After price confirmed, you can require for samples to check quality.
If you need the samples, we will charge for the sample cost. But the sample cost can be refundable when your quantity of first order is above the MOQ
Q: What is your main market?
R:Southeast Asia, South America,Middle East.North America,EU
After-sales Service
1 year warranty for all kinds of products;
If you find any defective accessories first time, we will give you the new parts for free to replace in the next order, as an experienced manufacturer, you can rest assured of the quality and after-sales service.
Established in 1998,DET motor is a professional manufacturer and exporter that is concerned with the design, development and production of motors. We are located in ZheJiang city, with convenient transportation access. All of our products comply with international quality standards and are greatly appreciated in a variety of different markets throughout the world.
We have over 550 employees, an annual sales figure that exceeds USD300,000,000 and are currently exporting 50% of our production worldwide. Our well-equipped facilities and excellent quality control throughout all stages of production enables us to guarantee total customer satisfaction.
As a result of our high quality products and outstanding customer service, we have gained a global sales network CZPT European.
If you are interested in any of our products or would like to discuss a custom order, please feel free to contact us. We are looking CZPT to forming successful business relationships with new clients around the world in the near future.
| Transfer | FOB/CIF |
| Payment | TT/LC/VISA/MASTER |
| Port | ZheJiang /HangZhou/HangZhou/HangZhou |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
| Samples: |
US$ 36/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
Basic knowledge of vacuum pump
A vacuum pump is a device that draws gas molecules from a sealed volume and maintains a partial vacuum. Its main job is to create a relative vacuum within a given volume or volumes. There are many types of vacuum pumps. This article will describe how they work, their types, and their applications.
How it works
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device that removes gas from a system by applying it to a higher pressure than the surrounding atmosphere. The working principle of the vacuum pump is based on the principle of gas transfer and entrapment. Vacuum pumps can be classified according to their vacuum level and the number of molecules that can be removed per cubic centimeter of space. In medium to high vacuum, viscous flow occurs when gas molecules collide with each other. Increasing the vacuum causes molecular or transitional flow.
A vacuum pump has several components that make it a versatile tool. One of the main components is the motor, which consists of a rotor and a stator. The rotor and stator contain coils that generate a magnetic field when excited. Both parts must be mounted on a base that supports the weight of the pump. There is also an oil drain that circulates oil throughout the system for lubrication and cooling purposes.
Another type of vacuum pump is the liquid ring vacuum pump. It works by positioning the impeller above or below the blades. Liquid ring pumps can also adjust the speed of the impeller. However, if you plan to use this type of pump, it is advisable to consult a specialist.
Vacuum pumps work by moving gas molecules to areas of higher or lower pressure. As the pressure decreases, the removal of the molecules becomes more difficult. Industrial vacuum systems require pumps capable of operating in the 1 to 10-6 Torr range.
Type
There are different types of vacuum pumps. They are used in many different applications, such as laboratories. The main purpose of these pumps is to remove air or gas molecules from the vacuum chamber. Different types of pumps use different techniques to achieve this. Some types of pumps use positive displacement, while others use liquid ring, molecular transfer, and entrapment techniques.
Some of these pumps are used in industrial processes, including making vacuum tubes, CRTs, electric lights, and semiconductor processing. They are also used in motor vehicles to power hydraulic components and aircraft. The gyroscope is usually controlled by these pumps. In some cases, they are also used in medical settings.
How a vacuum pump works depends on the type of gas being pumped. There are three main types: positive displacement, negative displacement, and momentum transfer. Depending on the type of lubrication, these principles can be further divided into different types of pumps. For example, dry vacuum pumps are less sensitive to gases and vapors.
Another type of vacuum pump is called a rotary vane pump. This type of pump has two main components, the rotor and the vacuum chamber. These pumps work by rotating moving parts against the pump casing. The mating surfaces of rotary pumps are designed with very small clearances to prevent fluid leakage to the low pressure side. They are suitable for vacuum applications requiring low pulsation and high continuous flow. However, they are not suitable for use with grinding media.
There are many types of vacuum pumps and it is important to choose the right one for your application. The type of pump depends on the needs and purpose of the system. The larger ones can work continuously, and the smaller ones are more suitable for intermittent use. 
Apply
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of industrial and scientific processes. For example, they are used in the production of vacuum tubes, CRTs, and electric lamps. They are also used in semiconductor processing. Vacuum pumps are also used as mechanical supports for other equipment. For example, there may be multiple vacuum pumps on the engine of a motor vehicle that powers the hydraulic components of an aircraft. In addition, they are often used in fusion research.
The most common type of vacuum pump used in the laboratory is the rotary vane pump. It works by directing airflow through a series of rotating blades in a circular housing. As the blades pass through the casing, they remove gas from the cavity and create a vacuum. Rotary pumps are usually single or double-stage and can handle pressures between 10 and 6 bar. It also has a high pumping speed.
Vacuum pumps are also used to fabricate solar cells on wafers. This involves a range of processes including doping, diffusion, dry etching, plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition, and bulk powder generation. These applications depend on the type of vacuum pump used in the process, and the vacuum pump chosen should be designed for the environment.
While there are several types of vacuum pumps available, their basic working principles remain the same. Each has different functions and capacities, depending on the type of vacuum. Generally divided into positive displacement pump, rotary vane pump, liquid ring pump, and molecular delivery pump.
Maintenance
The party responsible for general maintenance and repairs is the Principal Investigator (PI). Agknxs must be followed and approved by the PI and other relevant laboratory personnel. The Agknx provides guidelines for routine maintenance of vacuum pump equipment. Agknxs are not intended to replace detailed routine inspections of vacuum pump equipment, which should be performed by certified/qualified service personnel. If the device fails, the user should contact PI or RP for assistance.
First, check the vacuum pump for any loose parts. Make sure the inlet and outlet pressure gauges are open. When the proper pressure is shown, open the gate valve. Also, check the vacuum pump head and flow. Flow and head should be within the range indicated on the label. Bearing temperature should be within 35°F and maximum temperature should not exceed 80°F. The vacuum pump bushing should be replaced when it is severely worn.
If the vacuum pump has experienced several abnormal operating conditions, a performance test should be performed. Results should be compared to reference values to identify abnormalities. To avoid premature pump failure, a systematic approach to predictive maintenance is essential. This is a relatively new area in the semiconductor industry, but leading semiconductor companies and major vacuum pump suppliers have yet to develop a consistent approach.
A simplified pump-down test method is proposed to evaluate the performance of vacuum pumps. The method includes simulated aeration field tests and four pump performance indicators. Performance metrics are evaluated under gas-loaded, idle, and gas-load-dependent test conditions. 
Cost
The total cost of a vacuum pump consists of two main components: the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs. The latter is the most expensive component, as it consumes about four to five times the initial investment. Therefore, choosing a more energy-efficient model is a good way to reduce the total system cost and payback period.
The initial cost of a vacuum pump is about $786. Oil-lubricated rotary vane pumps are the cheapest, while oil-free rotary vane pumps are slightly more expensive. Non-contact pumps also cost slightly more. The cost of a vacuum pump is not high, but it is a factor that needs careful consideration.
When choosing a vacuum pump, it is important to consider the type of gas being pumped. Some pumps are only suitable for pumping air, while others are designed to pump helium. Oil-free air has a different pumping rate profile than air. Therefore, you need to consider the characteristics of the medium to ensure that the pump meets your requirements. The cost of a vacuum pump can be much higher than the purchase price, as the daily running and maintenance costs can be much higher.
Lubricated vacuum pumps tend to be more durable and less expensive, but they may require more maintenance. Maintenance costs will depend on the type of gas that needs to be pumped. Lighter gases need to be pumped slowly, while heavier gases need to be pumped faster. The maintenance level of a vacuum pump also depends on how often it needs to be lubricated.
Diaphragm vacuum pumps require regular maintenance and oil changes. The oil in the diaphragm pump should be changed every 3000 hours of use. The pump is also resistant to chemicals and corrosion. Therefore, it can be used in acidic and viscous products.


editor by CX 2024-03-29
China OEM 3 Phase Asynchronous AC Motor Vacuum Air Compressor Blower Pump Induction vacuum pump ac system
Product Description
3 Phase Asynchronous AC Motor Vacuum Air Compressor Blower Pump Induction Fan Motor
———————————————————————————————
Applications
Can be applied in the machines where continuous duty is required, typical applications like
- Pumps
- Fans
- Compressors
- Lifting equipment
- Production industry
General Description
- Frame sizes: 63 to 355M/L
- Rated output: 0.12 to 4-2012), low noise, little vibration, reliable running.
Optional Features
Electrical
Insulation Class:H
Thermal Protection:frame up to 132(include), with
PTC Thermistor, Thermostat or PT100
Mechanical
Others mountings
Protection Degree:IP56, IP65, IP66
Sealing:Lip seal, Oil seal
Space Heater, Double shaft ends
Drain HoleMounting Type
Conventional mounting type and suitable frame size are given in following table(with “√”)Frame basic type derived type B3 B5 B35 V1 V3 V5 V6 B6 B7 B8 V15 V36 B14 B34 V18 63~112 √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ 132~160 √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ – – – 180~280 √ √ √ √ – – – – – – – – – – – 315~355 √ – √ √ – – – – – – – – – – – If there is no other request in the order or agreement, terminal box standard position is at the right side of the frame; data above may be changed without prior notice
Site
Show Room
CertificatesPremium Service
Quality ControlWannan Motor Production Workshop and Flow Chart
Certificates and more COMPANY information please go to “ABOUT US”
—————————————————————————————————————————
Welcome to contact us directly…
wnmmotor
https://youtu.be/frVvg3yQqNMWANNAN MOTOR INDUSTRIAL SOLUTIONS
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Application: Industrial Speed: High Speed Number of Stator: Three-Phase Function: Driving, Control, 3 Phase Asynchronous AC Motor Casing Protection: Protection Type Number of Poles: 2.4.6.8.10.12 Samples: US$ 700/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order)|
Customization: Available|
What Are the Advantages of Using Oil-Sealed Vacuum Pumps?
Oil-sealed vacuum pumps offer several advantages in various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. High Vacuum Performance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are known for their ability to achieve high levels of vacuum. They can create and maintain deep vacuum levels, making them suitable for applications that require a low-pressure environment. The use of oil as a sealing and lubricating medium helps in achieving efficient vacuum performance.
2. Wide Operating Range: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps have a wide operating range, allowing them to handle a broad spectrum of vacuum levels. They can operate effectively in both low-pressure and high-vacuum conditions, making them versatile for different applications across various industries.
3. Efficient and Reliable Operation: These pumps are known for their reliability and consistent performance. The oil-sealed design provides effective sealing, preventing air leakage and maintaining a stable vacuum level. They are designed to operate continuously for extended periods without significant performance degradation, making them suitable for continuous industrial processes.
4. Contamination Handling: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are effective in handling certain types of contaminants that may be present in the process gases or air being evacuated. The oil acts as a barrier, trapping and absorbing certain particulates, moisture, and chemical vapors, preventing them from reaching the pump mechanism. This helps protect the pump internals from potential damage and contributes to the longevity of the pump.
5. Thermal Stability: The presence of oil in these pumps helps in dissipating heat generated during operation, contributing to their thermal stability. The oil absorbs and carries away heat, preventing excessive temperature rise within the pump. This thermal stability allows for consistent performance even during prolonged operation and helps protect the pump from overheating.
6. Noise Reduction: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps generally operate at lower noise levels compared to other types of vacuum pumps. The oil acts as a noise-damping medium, reducing the noise generated by the moving parts and the interaction of gases within the pump. This makes them suitable for applications where noise reduction is desired, such as laboratory environments or noise-sensitive industrial settings.
7. Versatility: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are versatile and can handle a wide range of gases and vapors. They can effectively handle both condensable and non-condensable gases, making them suitable for diverse applications in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and research laboratories.
8. Cost-Effective: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are often considered cost-effective options for many applications. They generally have a lower initial cost compared to some other types of high-vacuum pumps. Additionally, the maintenance and operating costs are relatively lower, making them an economical choice for industries that require reliable vacuum performance.
9. Simplicity and Ease of Maintenance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are relatively simple in design and easy to maintain. Routine maintenance typically involves monitoring oil levels, changing the oil periodically, and inspecting and replacing worn-out parts as necessary. The simplicity of maintenance procedures contributes to the overall cost-effectiveness and ease of operation.
10. Compatibility with Other Equipment: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are compatible with various process equipment and systems. They can be easily integrated into existing setups or used in conjunction with other vacuum-related equipment, such as vacuum chambers, distillation systems, or industrial process equipment.
These advantages make oil-sealed vacuum pumps a popular choice in many industries where reliable, high-performance vacuum systems are required. However, it’s important to consider specific application requirements and consult with experts to determine the most suitable type of vacuum pump for a particular use case.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in the Production of Solar Panels?
Yes, vacuum pumps are extensively used in the production of solar panels. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. The manufacturing process of solar panels involves several critical steps, many of which require the use of vacuum pumps. Vacuum technology plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency, reliability, and quality of solar panel production. Here are some key areas where vacuum pumps are utilized:
1. Silicon Ingot Production: The first step in solar panel manufacturing is the production of silicon ingots. These ingots are cylindrical blocks of pure crystalline silicon that serve as the raw material for solar cells. Vacuum pumps are used in the Czochralski process, which involves melting polycrystalline silicon in a quartz crucible and then slowly pulling a single crystal ingot from the molten silicon. Vacuum pumps create a controlled environment by removing impurities and preventing contamination during the crystal growth process.
2. Wafering: After the silicon ingots are produced, they undergo wafering, where the ingots are sliced into thin wafers. Vacuum pumps are used in wire saws to create a low-pressure environment that helps to cool and lubricate the cutting wire. The vacuum also assists in removing the silicon debris generated during the slicing process, ensuring clean and precise cuts.
3. Solar Cell Production: Vacuum pumps play a significant role in various stages of solar cell production. Solar cells are the individual units within a solar panel that convert sunlight into electricity. Vacuum pumps are used in the following processes:
– Diffusion: In the diffusion process, dopants such as phosphorus or boron are introduced into the silicon wafer to create the desired electrical properties. Vacuum pumps are utilized in the diffusion furnace to create a controlled atmosphere for the diffusion process and remove any impurities or gases that may affect the quality of the solar cell.
– Deposition: Thin films of materials such as anti-reflective coatings, passivation layers, and electrode materials are deposited onto the silicon wafer. Vacuum pumps are used in various deposition techniques like physical vapor deposition (PVD) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to create the necessary vacuum conditions for precise and uniform film deposition.
– Etching: Etching processes are employed to create the desired surface textures on the solar cell, which enhance light trapping and improve efficiency. Vacuum pumps are used in plasma etching or wet etching techniques to remove unwanted material or create specific surface structures on the solar cell.
4. Encapsulation: After the solar cells are produced, they are encapsulated to protect them from environmental factors such as moisture and mechanical stress. Vacuum pumps are used in the encapsulation process to create a vacuum environment, ensuring the removal of air and moisture from the encapsulation materials. This helps to achieve proper bonding and prevents the formation of bubbles or voids, which could degrade the performance and longevity of the solar panel.
5. Testing and Quality Control: Vacuum pumps are also utilized in testing and quality control processes during solar panel production. For example, vacuum systems can be used for leak testing to ensure the integrity of the encapsulation and to detect any potential defects or leaks in the panel assembly. Vacuum-based measurement techniques may also be employed for assessing the electrical characteristics and efficiency of the solar cells or panels.
In summary, vacuum pumps are integral to the production of solar panels. They are used in various stages of the manufacturing process, including silicon ingot production, wafering, solar cell production (diffusion, deposition, and etching), encapsulation, and testing. Vacuum technology enables precise control, contamination prevention, and efficient processing, contributing to the production of high-quality and reliable solar panels.
What Industries Commonly Rely on Vacuum Pump Technology?
Vacuum pump technology finds applications in various industries where creating and controlling vacuum or low-pressure environments is crucial. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Manufacturing and Production: Vacuum pumps are extensively used in manufacturing and production processes across multiple industries. They are employed for tasks such as vacuum molding, vacuum packaging, vacuum degassing, vacuum drying, and vacuum distillation. Industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and food processing rely on vacuum pump technology to achieve precise and controlled manufacturing conditions.
2. Chemical and Pharmaceutical: The chemical and pharmaceutical industries heavily rely on vacuum pumps for numerous applications. These include solvent recovery, vacuum filtration, vacuum drying, distillation, crystallization, and evaporation. Vacuum pumps enable these industries to carry out critical processes under reduced pressure, ensuring efficient separation, purification, and synthesis of various chemical compounds and pharmaceutical products.
3. Semiconductor and Electronics: The semiconductor and electronics industries extensively use vacuum pumps for manufacturing microchips, electronic components, and electronic devices. Vacuum pumps are crucial in processes such as physical vapor deposition (PVD), chemical vapor deposition (CVD), etching, ion implantation, and sputtering. These processes require controlled vacuum conditions to ensure precise deposition, surface modification, and contamination-free manufacturing.
4. Research and Development: Vacuum pump technology is integral to research and development activities across scientific disciplines. It supports experiments and investigations in fields such as physics, chemistry, materials science, biology, and environmental science. Vacuum pumps facilitate processes like freeze drying, vacuum distillation, vacuum evaporation, vacuum spectroscopy, and creating controlled atmospheric conditions for studying various phenomena.
5. Food and Beverage: The food and beverage industry relies on vacuum pumps for packaging and preservation purposes. Vacuum sealing is used to extend the shelf life of food products by removing air and creating a vacuum-sealed environment that inhibits spoilage and maintains freshness. Vacuum pumps are also used in processes like freeze drying, vacuum concentration, and vacuum cooling.
6. Oil and Gas: In the oil and gas industry, vacuum pumps play a role in various applications. They are used for crude oil vacuum distillation, vacuum drying, vapor recovery, gas compression, and gas stripping processes. Vacuum pumps help maintain optimal conditions during oil refining, gas processing, and petrochemical manufacturing.
7. Environmental and Waste Management: Vacuum pumps are employed in environmental and waste management applications. They are used for tasks such as soil vapor extraction, groundwater remediation, landfill gas recovery, and wastewater treatment. Vacuum pumps facilitate the removal and containment of gases, vapors, and pollutants, contributing to environmental protection and sustainable waste management.
8. Medical and Healthcare: The medical and healthcare sectors utilize vacuum pumps for various purposes. They are used in medical equipment such as vacuum-assisted wound therapy devices, vacuum-based laboratory analyzers, and vacuum suction systems in hospitals and clinics. Vacuum pumps are also used in medical research, pharmaceutical production, and medical device manufacturing.
9. Power Generation: Vacuum pumps play a role in power generation industries, including nuclear power plants and thermal power plants. They are used for steam condensation, turbine blade cooling, vacuum drying during transformer manufacturing, and vacuum systems for testing and maintenance of power plant equipment.
10. HVAC and Refrigeration: The HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries rely on vacuum pumps for system installation, maintenance, and repair. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate air and moisture from refrigerant lines and HVAC systems, ensuring optimal system performance and efficiency.
These are just a few examples of industries that commonly rely on vacuum pump technology. The versatility and wide-ranging applications of vacuum pumps make them indispensable tools across numerous sectors, enabling precise control over vacuum conditions, efficient manufacturing processes, and scientific investigations.


editor by CX 2024-03-20
China high quality AC Right Angle Gear Motor Reducer Fan Blower Vacuum Air Compressor Water Pump vacuum pump engine
Product Description
TaiBang Motor Industry Group Co., Ltd.
The main products is induction motor, reversible motor, DC brush gear motor, DC brushless gear motor , CH/CV big gear motors , Planetary gear motor ,Worm gear motor etc, which used widely in various fields of manufacturing pipelining, transportation, food, medicine, printing, fabric, packing, office, apparatus, entertainment etc, and is the preferred and matched product for automatic machine.
Motor Model Instruction
4RK25GN-C
| 4 | R | K | 25 | R | GN | C | |
| Frame Size | Type | Motor series | Power | Speed Control Motor |
Shaft Type | Voltage | Accessory |
| 2:60mm
3:70mm 4:80mm 5:90mm 6:104mm |
I:Induction
R:Reversible T:Torque |
K series | 6W
15W 25W 40W 60W 90W 120W 140W 180W 200W |
A:Round Shaft
GN:Bevel Gear Shaft GU:Bevel Gear Shaft |
A:Single Phase 110V
C:Single Phase 220V S:3-Phase 220V S3:3-Phase 380V S4:3-Phase 440V |
T/P:Thermally Protected
F:Fan M:Electro-magnetic |
Gear Head Model Instruction
4GN-100RC
| 4 | GN | 100 | K | |
| Frame Size | Shaft Type | Gear Reduction Ratio | Bearing Type | Other information |
| 2:60mm
3:70mm 4:80mm 5:90mm 6:104mm |
GN:Bevel Gear Shaft (60#,70#,80#,90# reduction gear head) GU:Bevel Gear Shaft GM:Intermediate Gear Head GS:Gearhead with ears |
1:100 | K:Standard Rolling Bearing
RT:Right Angle With Axile RC:Right Angle With Hollow Shaft |
Such as shaft diameter,shaft length,etc. |
Specification of motor 25W 80mm Fixed speed AC gear motor
| Type | Gear Tooth Output Shaft | Power (W) |
Frequency (Hz) |
Voltage (V) |
Current (A) |
Start Torque (g.cm) |
Rated | Gearbox Type | ||
| Torque (g.cm) |
Speed (rpm) |
Bearing Gearbox | Middle Gearbox | |||||||
| Reversible Motor | 4RK25GN-C | 25 | 50 | 220 | 0.30 | 1950 | 1950 | 1250 | 4GN/GU-K | 4GN10X |
| 25 | 60 | 220 | 0.27 | 1650 | 1620 | 1500 | 4GN/GU-K | 4GN10X | ||
Gear Head Torque Table(Kg.cm) (kg.cm×9.8÷100)=N.m
| Output Speed :RPM | 500 | 300 | 200 | 150 | 120 | 100 | 75 | 60 | 50 | 30 | 20 | 15 | 10 | 7.5 | 6 | 5 | 3 | ||
| Speed Ratio | 50Hz | 3 | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | 12.5 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 500 | |
| 60Hz | 3.6 | 6 | 9 | 15 | 18 | 30 | 36 | 60 | 90 | 120 | 180 | 300 | 360 | 600 | |||||
| Allowed Torque |
25W | kg.cm | 4 | 6.7 | 10 | 13.3 | 16 | 20 | 26.7 | 32 | 39 | 65 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 |
| 30W | kg.cm | 4.8 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 24 | 32 | 38 | 46 | 76 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | |
| 40W | kg.cm | 6.7 | 11 | 16 | 21.3 | 28 | 33 | 42 | 54 | 65 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | |
| Note: Speed figures are based on synchronous speed, The actual output speed, under rated torque conditions, is about 10-20% less than synchronous speed, a grey background indicates output shaft of geared motor rotates in the same direction as output shaft of motor. A white background indicates rotates rotation in the opposite direction. | |||||||||||||||||||
External Dimension
4I(R)K25/4A(GN)( )
| Type | Reduction Ratio | L1 mm |
L2 mm |
L3 mm |
| 4RK25GN | 1:3~1:20 | 86 | 32 | 118 |
| 1:25~1:180 | 85 | 44 | 130 |
4I(R)K25/4GN( )RC
4I(R)K25/4GN( )RT
Above drawing is for standard screw hole.If need through hole, terminal box, or electronic magnet brake, need to tell the seller.
Connection Diagram:
FAQ
Q: How about your company?
A:We are gear motor factory located in HangZhou city of China,we start from 1995 ,we have more than 1200 workers ,main products is AC micro gear motor 6W to 250W, AC small gear motor 100W to 3700W,brush DC motor 10W to 400W,brushless motor 10W to 750W,drum motor 60W to 3700W ,Planetary gearbox ,worm gearbox etc .
Q: How to choose a suitable motor?
A:If you have gear motor pictures or drawings to show us, or you tell us detailed specs like voltage, speed, torque, motor size, working mode of the motor, needed lifetime and noise level etc, please do not hesitate to let us know, then we can suggest suitable motor per your request .
Q: Can you make the gear motor with customize specifications ?
Yes, we can customize per your request for the voltage, speed, torque and shaft size and shape. If you need additional wires or cables soldered on the terminal or need to add connectors, or capacitors or EMC we can make it too.
Q: What’s your lead time?
A: Usually our regular standard product will need 10-15days, a bit longer for customized products. But we are very flexible on the lead time, it will depend on the specific orders.
Q: What is your MOQ?
A: If delivery by sea ,the minimum order is 100 pieces, if deliver by express, there is no limit.
Q: Do you have the item in stock?
A: I am sorry we do not have the item in stock, All products are made with orders.
Q: How to contact us ?
A: You can send us enquiry . /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Single-Phase |
| Function: | Driving, Control |
| Casing Protection: | Closed Type |
| Number of Poles: | 4 |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How Do You Maintain and Troubleshoot Vacuum Pumps?
Maintaining and troubleshooting vacuum pumps is essential to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Maintenance of Vacuum Pumps:
1. Regular Inspection: Perform regular visual inspections of the pump to check for any signs of damage, leaks, or abnormal wear. Inspect the motor, belts, couplings, and other components for proper alignment and condition.
2. Lubrication: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for lubrication. Some vacuum pumps require regular oil changes or lubrication of moving parts. Ensure that the correct type and amount of lubricant are used.
3. Oil Level Check: Monitor the oil level in oil-sealed pumps and maintain it within the recommended range. Add or replace oil as necessary, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
4. Filter Maintenance: Clean or replace filters regularly to prevent clogging and ensure proper airflow. Clogged filters can impair pump performance and increase energy consumption.
5. Cooling System: If the vacuum pump has a cooling system, inspect it regularly for cleanliness and proper functioning. Clean or replace cooling components as needed to prevent overheating.
6. Seals and Gaskets: Check the seals and gaskets for signs of wear or leakage. Replace any damaged or worn seals promptly to maintain airtightness.
7. Valve Maintenance: If the vacuum pump includes valves, inspect and clean them regularly to ensure proper operation and prevent blockages.
8. Vibration and Noise: Monitor the pump for excessive vibration or unusual noise, which may indicate misalignment, worn bearings, or other mechanical issues. Address these issues promptly to prevent further damage.
Troubleshooting Vacuum Pump Problems:
1. Insufficient Vacuum Level: If the pump is not achieving the desired vacuum level, check for leaks in the system, improper sealing, or worn-out seals. Inspect valves, connections, and seals for leaks and repair or replace as needed.
2. Poor Performance: If the pump is not providing adequate performance, check for clogged filters, insufficient lubrication, or worn-out components. Clean or replace filters, ensure proper lubrication, and replace worn parts as necessary.
3. Overheating: If the pump is overheating, check the cooling system for blockages or insufficient airflow. Clean or replace cooling components and ensure proper ventilation around the pump.
4. Excessive Noise or Vibration: Excessive noise or vibration may indicate misalignment, worn bearings, or other mechanical issues. Inspect and repair or replace damaged or worn parts. Ensure proper alignment and balance of rotating components.
5. Motor Issues: If the pump motor fails to start or operates erratically, check the power supply, electrical connections, and motor components. Test the motor using appropriate electrical testing equipment and consult an electrician or motor specialist if necessary.
6. Excessive Oil Consumption: If the pump is consuming oil at a high rate, check for leaks or other issues that may be causing oil loss. Inspect seals, gaskets, and connections for leaks and repair as needed.
7. Abnormal Odors: Unusual odors, such as a burning smell, may indicate overheating or other mechanical problems. Address the issue promptly and consult a technician if necessary.
8. Manufacturer Guidelines: Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance and troubleshooting specific to your vacuum pump model. Follow the prescribed maintenance schedule and seek professional assistance when needed.
By following proper maintenance procedures and promptly addressing any troubleshooting issues, you can ensure the reliable operation and longevity of your vacuum pump.

How Do Vacuum Pumps Assist in Freeze-Drying Processes?
Freeze-drying, also known as lyophilization, is a dehydration technique used in various industries, including pharmaceutical manufacturing. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in facilitating freeze-drying processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
During freeze-drying, vacuum pumps assist in the removal of water or solvents from pharmaceutical products while preserving their structure and integrity. The freeze-drying process involves three main stages: freezing, primary drying (sublimation), and secondary drying (desorption).
1. Freezing: In the first stage, the pharmaceutical product is frozen to a solid state. Freezing is typically achieved by lowering the temperature of the product below its freezing point. The frozen product is then placed in a vacuum chamber.
2. Primary Drying (Sublimation): Once the product is frozen, the vacuum pump creates a low-pressure environment within the chamber. By reducing the pressure, the boiling point of water or solvents present in the frozen product is lowered, allowing them to transition directly from the solid phase to the vapor phase through a process called sublimation. Sublimation bypasses the liquid phase, preventing potential damage to the product’s structure.
The vacuum pump maintains a low-pressure environment by continuously removing the water vapor or solvent vapor generated during sublimation. The vapor is drawn out of the chamber, leaving behind the freeze-dried product. This process preserves the product’s original form, texture, and biological activity.
3. Secondary Drying (Desorption): After the majority of the water or solvents have been removed through sublimation, the freeze-dried product may still contain residual moisture or solvents. In the secondary drying stage, the vacuum pump continues to apply vacuum to the chamber, but at a higher temperature. The purpose of this stage is to remove the remaining moisture or solvents through evaporation.
The vacuum pump maintains the low-pressure environment, allowing the residual moisture or solvents to evaporate at a lower temperature than under atmospheric pressure. This prevents potential thermal degradation of the product. Secondary drying further enhances the stability and shelf life of the freeze-dried pharmaceutical product.
By creating and maintaining a low-pressure environment, vacuum pumps enable efficient and controlled sublimation and desorption during the freeze-drying process. They facilitate the removal of water or solvents while minimizing the potential damage to the product’s structure and preserving its quality. Vacuum pumps also contribute to the overall speed and efficiency of the freeze-drying process by continuously removing the vapor generated during sublimation and evaporation. The precise control provided by vacuum pumps ensures the production of stable and high-quality freeze-dried pharmaceutical products.

How Do You Choose the Right Size Vacuum Pump for a Specific Application?
Choosing the right size vacuum pump for a specific application involves considering several factors to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Required Vacuum Level: The first consideration is the desired vacuum level for your application. Different applications have varying vacuum level requirements, ranging from low vacuum to high vacuum or even ultra-high vacuum. Determine the specific vacuum level needed, such as microns of mercury (mmHg) or pascals (Pa), and choose a vacuum pump capable of achieving and maintaining that level.
2. Pumping Speed: The pumping speed, also known as the displacement or flow rate, is the volume of gas a vacuum pump can remove from a system per unit of time. It is typically expressed in liters per second (L/s) or cubic feet per minute (CFM). Consider the required pumping speed for your application, which depends on factors such as the volume of the system, the gas load, and the desired evacuation time.
3. Gas Load and Composition: The type and composition of the gas or vapor being pumped play a significant role in selecting the right vacuum pump. Different pumps have varying capabilities and compatibilities with specific gases. Some pumps may be suitable for pumping only non-reactive gases, while others can handle corrosive gases or vapors. Consider the gas load and its potential impact on the pump’s performance and materials of construction.
4. Backing Pump Requirements: In some applications, a vacuum pump may require a backing pump to reach and maintain the desired vacuum level. A backing pump provides a rough vacuum, which is then further processed by the primary vacuum pump. Consider whether your application requires a backing pump and ensure compatibility and proper sizing between the primary pump and the backing pump.
5. System Leakage: Evaluate the potential leakage in your system. If your system has significant leakage, you may need a vacuum pump with a higher pumping speed to compensate for the continuous influx of gas. Additionally, consider the impact of leakage on the required vacuum level and the pump’s ability to maintain it.
6. Power Requirements and Operating Cost: Consider the power requirements of the vacuum pump and ensure that your facility can provide the necessary electrical supply. Additionally, assess the operating cost, including energy consumption and maintenance requirements, to choose a pump that aligns with your budget and operational considerations.
7. Size and Space Constraints: Take into account the physical size of the vacuum pump and whether it can fit within the available space in your facility. Consider factors such as pump dimensions, weight, and the need for any additional accessories or support equipment.
8. Manufacturer’s Recommendations and Expert Advice: Consult the manufacturer’s specifications, guidelines, and recommendations for selecting the right pump for your specific application. Additionally, seek expert advice from vacuum pump specialists or engineers who can provide insights based on their experience and knowledge.
By considering these factors and evaluating the specific requirements of your application, you can select the right size vacuum pump that meets the desired vacuum level, pumping speed, gas compatibility, and other essential criteria. Choosing the appropriate vacuum pump ensures efficient operation, optimal performance, and longevity for your application.


editor by CX 2024-03-06
China Hot selling 1HP 750W 220V 110vsilent Oil-Free Vacuum Pump Copper Wire High-Grade Motor Works Continuously for 24 Hours, Made in China vacuum pump design
Product Description
| Model | BST80AFZ/BSZ |
| Voltage/frequency (V/Hz) | 220-240V/50Hz; 110-115v/60Hz |
| Input power(W) | 50-80 |
| Speed (r/min) | ≥1380 1650 |
| Primary vacuumKPa | -90KPa |
| Secondary vacuumKPa | -98KPa |
| Restart pressure (KPa) | 0KPa |
| Rated volume flow (m3/h) | 2.1m3/h@0KPa; |
| Noise dB(A) | ≤42dB(A) |
| Ambient temperature ºC | -5~40 ºC |
| Insulation Class | B |
| Cold insulation resistance (MΩ) | ≥100MΩ |
| Voltage resistance | 1500V/50Hz 1min (No breakdown) |
| Thermal protector | Automatic reset 135±5ºC |
| Capacitance (μF) | 4μF±5% 10μF±5% |
| Net weight (Kg) | 2.2Kg |
| Installation Dimensions (mm) | 60×77 4*M5 |
| External Dimensions (mm) | 140*89*116mm |
| Typical application | |
| Respirator (ventilator) | oxygenerator |
| Disinfectant sprayer | Blood analyzer |
| Clinical aspirator | Dialysis / hemodialysis |
| Dental vacuum drying oven | Air suspension system |
| Vending machines / coffee blenders and coffee machines | Massage chair |
| Chromatographic analyzer | Teaching instrument platform |
| On board access control system | Airborne oxygen generator |
Why choose CHINAMFG air compressor
1. It saves 10-30% energy than the air compressor produced by ordinary manufacturers.
2. It is widely used in medical oxygen generator and ventilator .
3. A large number of high-speed train and automobile application cases, supporting – 41 to 70 ºC, 0-6000 CHINAMFG above sea level .
4. Medium and high-end quality, with more than 7000 hours of trouble free operation for conventional products and more than 15000 hours of trouble free operation for high-end products.
5. Simple operation, convenient maintenance and remote guidance.
6. Faster delivery time, generally completed within 25 days within 1000 PCs.
Machine Parts
Name: Motor
Brand: COMBESTAIR
Original: China
1.The coil adopts the fine pure copper enameled wire, and the rotor adopts the famous brand silicon steel sheet such as ZheJiang baosteel.
2.The customer can choose the insulation grade B or F motor according to What he wants.
3.The motor has a built-in thermal protector, which can select external heat sensor.
4.Voltage from AC100V ~120V, 200V ~240V, 50Hz / 60Hz, DC6V~200V optional ; AC motor can choose double voltage double frequency ; DC Motor can choose the control of the infinitely variable speed.
Machine Parts
Name: Bearing
Brand: ERB , CHINAMFG , NSK
Original: China ect.
1.Standard products choose the special bearing ‘ERB’ in oil-free compressor, and the environment temperature tolerance from -50ºC to 180 ºC . Ensure no fault operation for 20,000 hours.
2.Customers can select TPI, NSK and other imported bearings according to the working condition.
Machine Parts
Name: Valve plates
Brand: SANDVIK
Original: Sweden
1.Custom the valve steel of Sweden SANDVIK; Good flexibility and long durability.
2.Thickness from 0.08mm to 1.2mm, suitable for maximum pressure from 0.8 MPa to 1.2 MPa.
Machine Parts
Name: Piston ring
Brand: COMBESTAIR-OEM , Saint-Gobain
Original: China , France
1.Using domestic famous brand–Polytetrafluoroethylene composite material; Wear-resistant high temperature; Ensure more than 10,000 hours of service life.
2.High-end products: you can choose the ST.gobain’s piston ring from the American import.
| serial number |
Code number | Name and specification | Quantity | Material | Note |
| 1 | 212571109 | Fan cover | 2 | Reinforced nylon 1571 | |
| 2 | 212571106 | Left fan | 1 | Reinforced nylon 1571 | |
| 3 | 212571101 | Left box | 1 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL104 | |
| 4 | 212571301 | Connecting rod | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL104 | |
| 5 | 212571304 | Piston cup | 2 | PHB filled PTFE | |
| 6 | 212571302 | Clamp | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL102 | |
| 7 | 7050616 | Screw of cross head | 2 | Carbon structural steel of cold heading | M6•16 |
| 8 | 212571501 | Air cylinder | 2 | Thin wall pipe of aluninun alloy 6A02T4 | |
| 9 | 17103 | Seal ring of Cylinder | 2 | Silicone rubber | |
| 10 | 212571417 | Sealing ring of cylinder cover | 2 | Silicone rubber | |
| 11 | 212571401 | Cylinder head | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL102 | |
| 12 | 7571525 | Screw of inner hexagon Cylinder head | 12 | M5•25 | |
| 13 | 17113 | Sealing ring of connecting pipe | 4 | Silicong rubber | |
| 14 | 212571801 | Connecting pipe | 2 | Aluminum and aluminum alloy connecting rod LY12 | |
| 15 | 7100406 | Screw of Cross head | 4 | 1Cr13N19 | M4•6 |
| 16 | 212571409 | Limit block | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL102 | |
| 17 | 000402.2 | Air outlet valve | 2 | 7Cr27 quenching steel belt of The Swedish sandvik | |
| 18 | 212571403 | valve | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL102 | |
| 19 | 212571404 | Air inlet valve | 2 | 7Cr27 quenching steel belt of The Swedish sandvik | |
| 20 | 212571406 | Metal gasket | 2 | Stainless steel plate of heat and acidresistance | |
| 21 | 212571107 | Right fan | 1 | Reinforced nylon 1571 | |
| 22 | 212571201 | Crank | 2 | Gray castiron H20-40 | |
| 23 | 14040 | Bearing 6006-2Z | 2 | ||
| 24 | 70305 | Tighten screw of inner hexagon flat end | 2 | M8•8 | |
| 25 | 7571520 | Screw of inner hexagon Cylinder head | 2 | M5•20 | |
| 26 | 212571102 | Right box | 1 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL104 | |
| 27 | 6P-4 | Lead protective ring | 1 | ||
| 28 | 7095712-211 | Hexagon head bolt | 2 | Carbon structural steel of cold heading | M5•152 |
| 29 | 715710-211 | Screw of Cross head | 2 | Carbon structural steel of cold heading | M5•120 |
| 30 | 16602 | Light spring washer | 4 | ø5 | |
| 31 | 212571600 | Stator | 1 | ||
| 32 | 70305 | Lock nut of hexagon flange faces | 2 | ||
| 33 | 212571700 | Rotor | 1 | ||
| 34 | 14032 | Bearing 6203-2Z | 2 |
FAQ
Q1: Are you factory or trade company?
A1: We are factory.
Q2: What the exactly address of your factory?
A2: Our factory is located in Linbei industrial area No.30 HangZhou City of ZHangZhoug Province, China
Q3: Warranty terms of your machine?
A3: Two years warranty for the machine and technical support according to your needs.
Q4: Will you provide some spare parts of the machines?
A4: Yes, of course.
Q5: How long will you take to arrange production?
A5: Generally, 1000 pcs can be delivered within 25 days
Q6: Can you accept OEM orders?
A6: Yes, with professional design team, OEM orders are highly welcome
Q7:Can you accept non-standard customization?
A7:We have the ability to develop new products and can customize, develop and research according to your requirements
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Remote Guided Maintenance |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 2 Years |
| Principle: | Mixed-Flow Compressor |
| Application: | Back Pressure Type, Intermediate Back Pressure Type, High Back Pressure Type, Low Back Pressure Type |
| Performance: | Low Noise, Variable Frequency, Explosion-Proof |
| Mute: | Mute |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Are the Advantages of Using Oil-Sealed Vacuum Pumps?
Oil-sealed vacuum pumps offer several advantages in various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. High Vacuum Performance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are known for their ability to achieve high levels of vacuum. They can create and maintain deep vacuum levels, making them suitable for applications that require a low-pressure environment. The use of oil as a sealing and lubricating medium helps in achieving efficient vacuum performance.
2. Wide Operating Range: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps have a wide operating range, allowing them to handle a broad spectrum of vacuum levels. They can operate effectively in both low-pressure and high-vacuum conditions, making them versatile for different applications across various industries.
3. Efficient and Reliable Operation: These pumps are known for their reliability and consistent performance. The oil-sealed design provides effective sealing, preventing air leakage and maintaining a stable vacuum level. They are designed to operate continuously for extended periods without significant performance degradation, making them suitable for continuous industrial processes.
4. Contamination Handling: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are effective in handling certain types of contaminants that may be present in the process gases or air being evacuated. The oil acts as a barrier, trapping and absorbing certain particulates, moisture, and chemical vapors, preventing them from reaching the pump mechanism. This helps protect the pump internals from potential damage and contributes to the longevity of the pump.
5. Thermal Stability: The presence of oil in these pumps helps in dissipating heat generated during operation, contributing to their thermal stability. The oil absorbs and carries away heat, preventing excessive temperature rise within the pump. This thermal stability allows for consistent performance even during prolonged operation and helps protect the pump from overheating.
6. Noise Reduction: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps generally operate at lower noise levels compared to other types of vacuum pumps. The oil acts as a noise-damping medium, reducing the noise generated by the moving parts and the interaction of gases within the pump. This makes them suitable for applications where noise reduction is desired, such as laboratory environments or noise-sensitive industrial settings.
7. Versatility: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are versatile and can handle a wide range of gases and vapors. They can effectively handle both condensable and non-condensable gases, making them suitable for diverse applications in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and research laboratories.
8. Cost-Effective: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are often considered cost-effective options for many applications. They generally have a lower initial cost compared to some other types of high-vacuum pumps. Additionally, the maintenance and operating costs are relatively lower, making them an economical choice for industries that require reliable vacuum performance.
9. Simplicity and Ease of Maintenance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are relatively simple in design and easy to maintain. Routine maintenance typically involves monitoring oil levels, changing the oil periodically, and inspecting and replacing worn-out parts as necessary. The simplicity of maintenance procedures contributes to the overall cost-effectiveness and ease of operation.
10. Compatibility with Other Equipment: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are compatible with various process equipment and systems. They can be easily integrated into existing setups or used in conjunction with other vacuum-related equipment, such as vacuum chambers, distillation systems, or industrial process equipment.
These advantages make oil-sealed vacuum pumps a popular choice in many industries where reliable, high-performance vacuum systems are required. However, it’s important to consider specific application requirements and consult with experts to determine the most suitable type of vacuum pump for a particular use case.

Considerations for Selecting a Vacuum Pump for Cleanroom Applications
When it comes to selecting a vacuum pump for cleanroom applications, several considerations should be taken into account. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Cleanrooms are controlled environments used in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and microelectronics. These environments require strict adherence to cleanliness and particle control standards to prevent contamination of sensitive processes or products. Selecting the right vacuum pump for cleanroom applications is crucial to maintain the required level of cleanliness and minimize the introduction of contaminants. Here are some key considerations:
1. Cleanliness: The cleanliness of the vacuum pump is of utmost importance in cleanroom applications. The pump should be designed and constructed to minimize the generation and release of particles, oil vapors, or other contaminants into the cleanroom environment. Oil-free or dry vacuum pumps are commonly preferred in cleanroom applications as they eliminate the risk of oil contamination. Additionally, pumps with smooth surfaces and minimal crevices are easier to clean and maintain, reducing the potential for particle buildup.
2. Outgassing: Outgassing refers to the release of gases or vapors from the surfaces of materials, including the vacuum pump itself. In cleanroom applications, it is crucial to select a vacuum pump with low outgassing characteristics to prevent the introduction of contaminants into the environment. Vacuum pumps specifically designed for cleanroom use often undergo special treatments or use materials with low outgassing properties to minimize this effect.
3. Particle Generation: Vacuum pumps can generate particles due to the friction and wear of moving parts, such as rotors or vanes. These particles can become a source of contamination in cleanrooms. When selecting a vacuum pump for cleanroom applications, it is essential to consider the pump’s particle generation level and choose pumps that have been designed and tested to minimize particle emissions. Pumps with features like self-lubricating materials or advanced sealing mechanisms can help reduce particle generation.
4. Filtration and Exhaust Systems: The filtration and exhaust systems associated with the vacuum pump are critical for maintaining cleanroom standards. The vacuum pump should be equipped with efficient filters that can capture and remove any particles or contaminants generated during operation. High-quality filters, such as HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters, can effectively trap even the smallest particles. The exhaust system should be properly designed to ensure that filtered air is released outside the cleanroom or passes through additional filtration before being reintroduced into the environment.
5. Noise and Vibrations: Noise and vibrations generated by vacuum pumps can have an impact on cleanroom operations. Excessive noise can affect the working environment and compromise communication, while vibrations can potentially disrupt sensitive processes or equipment. It is advisable to choose vacuum pumps specifically designed for quiet operation and that incorporate measures to minimize vibrations. Pumps with noise-dampening features and vibration isolation systems can help maintain a quiet and stable cleanroom environment.
6. Compliance with Standards: Cleanroom applications often have specific industry standards or regulations that must be followed. When selecting a vacuum pump, it is important to ensure that it complies with relevant cleanroom standards and requirements. Considerations may include ISO cleanliness standards, cleanroom classification levels, and industry-specific guidelines for particle count, outgassing levels, or allowable noise levels. Manufacturers that provide documentation and certifications related to cleanroom suitability can help demonstrate compliance.
7. Maintenance and Serviceability: Proper maintenance and regular servicing of vacuum pumps are essential for their reliable and efficient operation. When choosing a vacuum pump for cleanroom applications, consider factors such as ease of maintenance, availability of spare parts, and access to service and support from the manufacturer. Pumps with user-friendly maintenance features, clear service instructions, and a responsive customer support network can help minimize downtime and ensure continued cleanroom performance.
In summary, selecting a vacuum pump for cleanroom applications requires careful consideration of factors such as cleanliness, outgassing characteristics, particle generation, filtration and exhaust systems, noise and vibrations, compliance with standards, and maintenance requirements. By choosing vacuum pumps designed specifically for cleanroom use and considering these key factors, cleanroom operators can maintain the required level of cleanliness and minimize the risk of contamination in their critical processes and products.

What Are the Primary Applications of Vacuum Pumps?
Vacuum pumps have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Industrial Processes:
Vacuum pumps play a vital role in numerous industrial processes, including:
– Vacuum Distillation: Vacuum pumps are used in distillation processes to lower the boiling points of substances, enabling separation and purification of various chemicals and compounds.
– Vacuum Drying: Vacuum pumps aid in drying processes by creating a low-pressure environment, which accelerates moisture removal from materials without excessive heat.
– Vacuum Packaging: Vacuum pumps are used in the food industry to remove air from packaging containers, prolonging the shelf life of perishable goods by reducing oxygen exposure.
– Vacuum Filtration: Filtration processes can benefit from vacuum pumps to enhance filtration rates by applying suction, facilitating faster separation of solids and liquids.
2. Laboratory and Research:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories and research facilities for various applications:
– Vacuum Chambers: Vacuum pumps create controlled low-pressure environments within chambers for conducting experiments, testing materials, or simulating specific conditions.
– Mass Spectrometry: Mass spectrometers often utilize vacuum pumps to create the necessary vacuum conditions for ionization and analysis of samples.
– Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps enable freeze-drying processes, where samples are frozen and then subjected to a vacuum, allowing the frozen water to sublimate directly from solid to vapor state.
– Electron Microscopy: Vacuum pumps are essential for electron microscopy techniques, providing the necessary vacuum environment for high-resolution imaging of samples.
3. Semiconductor and Electronics Industries:
High vacuum pumps are critical in the semiconductor and electronics industries for manufacturing and testing processes:
– Semiconductor Fabrication: Vacuum pumps are used in various stages of chip manufacturing, including deposition, etching, and ion implantation processes.
– Thin Film Deposition: Vacuum pumps create the required vacuum conditions for depositing thin films of materials onto substrates, as done in the production of solar panels, optical coatings, and electronic components.
– Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are utilized in leak testing applications to detect and locate leaks in electronic components, systems, or pipelines.
4. Medical and Healthcare:
Vacuum pumps have several applications in the medical and healthcare sectors:
– Vacuum Assisted Wound Closure: Vacuum pumps are used in negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), where they create a controlled vacuum environment to promote wound healing and removal of excess fluids.
– Laboratory Equipment: Vacuum pumps are essential in medical and scientific equipment such as vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, and centrifugal concentrators.
– Anesthesia and Medical Suction: Vacuum pumps are utilized in anesthesia machines and medical suction devices to create suction and remove fluids or gases from the patient’s body.
5. HVAC and Refrigeration:
Vacuum pumps are employed in the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries:
– Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems: Vacuum pumps are used during system installation, maintenance, and repair to evacuate moisture and air from refrigeration and air conditioning systems, ensuring efficient operation.
– Vacuum Insulation Panels: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the manufacturing of vacuum insulation panels, which offer superior insulation properties for buildings and appliances.
6. Power Generation:
Vacuum pumps play a role in power generation applications:
– Steam Condenser Systems: Vacuum pumps are used in power plants to remove non-condensable gases from steam condenser systems, improving thermal efficiency.
– Gas Capture: Vacuum pumps are utilized to capture and remove gases, such as hydrogen or helium, in nuclear power plants, research reactors, or particle accelerators.
These are just a few examples of the primary applications of vacuum pumps. The versatility and wide range of vacuum pump types make them essential in numerous industries, contributing to various manufacturing processes, research endeavors, and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2024-01-01
China Standard OEM Custom Small No – Oil Vacuum Pump AC Motor Negative Pressure Suction Pump 400W Pompe à Vide Sans Huiles CE TUV Certification Ue with Great quality
Product Description
|
Model |
BST400AFZ/BSZ |
|
Voltage/frequency (V/Hz) |
220-240V/50Hz 100v-120v/60Hz |
|
Input power(W) |
≤300 |
|
Speed (r/min) |
≥1350 1650 |
|
Primary vacuumKPa |
-94KPa |
|
Secondary vacuumKPa |
-100KPa |
|
Restart pressure (KPa) |
0KPa |
|
Rated volume flow (m3/h) |
≥7.0m3/h @0KPa; |
|
Noise dB(A) |
≤55dB(A) |
|
Ambient temperature ºC |
-5~40 ºC |
|
Insulation Class |
B |
|
Cold insulation resistance (MΩ) |
≥100MΩ |
|
Voltage resistance |
1500V/50Hz 1min (No breakdown) |
|
Thermal protector |
Automatic reset 135±5ºC |
|
Capacitance (μF) |
15μF±5% 45μF±5% |
|
Net weight (Kg) |
7.8Kg |
|
Installation Dimensions (mm) |
203.2×88.9mm(Install thread 4-M6) |
|
External Dimensions (mm) |
244.5*128*177mm |
| Typical application | |
| Respirator (ventilator) | oxygenerator |
| Disinfectant sprayer | Blood analyzer |
| Clinical aspirator | Dialysis / hemodialysis |
| Dental vacuum drying oven | Air suspension system |
| Vending machines / coffee blenders and coffee machines | Massage chair |
| Chromatographic analyzer | Teaching instrument platform |
| On board access control system | Airborne oxygen generator |
Why choose CHINAMFG air compressor
1. It saves 10-30% energy than the air compressor produced by ordinary manufacturers.
2. It is widely used in medical oxygen generator and ventilator .
3. A large number of high-speed train and automobile application cases, supporting – 41 to 70 ºC, 0-6000 CHINAMFG above sea level .
4. Medium and high-end quality, with more than 7000 hours of trouble free operation for conventional products and more than 15000 hours of trouble free operation for high-end products.
5. Simple operation, convenient maintenance and remote guidance.
6. Faster delivery time, generally completed within 25 days within 1000 PCs.
Machine Parts
Name: Motor
Brand: COMBESTAIR
Original: China
1.The coil adopts the fine pure copper enameled wire, and the rotor adopts the famous brand silicon steel sheet such as ZheJiang baosteel.
2.The customer can choose the insulation grade B or F motor according to What he wants.
3.The motor has a built-in thermal protector, which can select external heat sensor.
4.Voltage from AC100V ~120V, 200V ~240V, 50Hz / 60Hz, DC6V~200V optional ; AC motor can choose double voltage double frequency ; DC Motor can choose the control of the infinitely variable speed.
Machine Parts
Name: Bearing
Brand: ERB , CHINAMFG , NSK
Original: China ect.
1.Standard products choose the special bearing ‘ERB’ in oil-free compressor, and the environment temperature tolerance from -50ºC to 180 ºC . Ensure no fault operation for 20,000 hours.
2.Customers can select TPI, NSK and other imported bearings according to the working condition.
Machine Parts
Name: Valve plates
Brand: SANDVIK
Original: Sweden
1.Custom the valve steel of Sweden SANDVIK; Good flexibility and long durability.
2.Thickness from 0.08mm to 1.2mm, suitable for maximum pressure from 0.8 MPa to 1.2 MPa.
Machine Parts
Name: Piston ring
Brand: COMBESTAIR-OEM , Saint-Gobain
Original: China , France
1.Using domestic famous brand–Polytetrafluoroethylene composite material; Wear-resistant high temperature; Ensure more than 10,000 hours of service life.
2.High-end products: you can choose the ST.gobain’s piston ring from the American import.
| serial number |
Code number | Name and specification | Quantity | Material | Note |
| 1 | 212571109 | Fan cover | 2 | Reinforced nylon 1571 | |
| 2 | 212571106 | Left fan | 1 | Reinforced nylon 1571 | |
| 3 | 212571101 | Left box | 1 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL104 | |
| 4 | 212571301 | Connecting rod | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL104 | |
| 5 | 212571304 | Piston cup | 2 | PHB filled PTFE | |
| 6 | 212571302 | Clamp | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL102 | |
| 7 | 7050616 | Screw of cross head | 2 | Carbon structural steel of cold heading | M6•16 |
| 8 | 212571501 | Air cylinder | 2 | Thin wall pipe of aluninun alloy 6A02T4 | |
| 9 | 17103 | Seal ring of Cylinder | 2 | Silicone rubber | |
| 10 | 212571417 | Sealing ring of cylinder cover | 2 | Silicone rubber | |
| 11 | 212571401 | Cylinder head | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL102 | |
| 12 | 7571525 | Screw of inner hexagon Cylinder head | 12 | M5•25 | |
| 13 | 17113 | Sealing ring of connecting pipe | 4 | Silicong rubber | |
| 14 | 212571801 | Connecting pipe | 2 | Aluminum and aluminum alloy connecting rod LY12 | |
| 15 | 7100406 | Screw of Cross head | 4 | 1Cr13N19 | M4•6 |
| 16 | 212571409 | Limit block | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL102 | |
| 17 | 000402.2 | Air outlet valve | 2 | 7Cr27 quenching steel belt of The Swedish sandvik | |
| 18 | 212571403 | valve | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL102 | |
| 19 | 212571404 | Air inlet valve | 2 | 7Cr27 quenching steel belt of The Swedish sandvik | |
| 20 | 212571406 | Metal gasket | 2 | Stainless steel plate of heat and acidresistance | |
| 21 | 212571107 | Right fan | 1 | Reinforced nylon 1571 | |
| 22 | 212571201 | Crank | 2 | Gray castiron H20-40 | |
| 23 | 14040 | Bearing 6006-2Z | 2 | ||
| 24 | 70305 | Tighten screw of inner hexagon flat end | 2 | M8•8 | |
| 25 | 7571520 | Screw of inner hexagon Cylinder head | 2 | M5•20 | |
| 26 | 212571102 | Right box | 1 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL104 | |
| 27 | 6P-4 | Lead protective ring | 1 | ||
| 28 | 7095712-211 | Hexagon head bolt | 2 | Carbon structural steel of cold heading | M5•152 |
| 29 | 715710-211 | Screw of Cross head | 2 | Carbon structural steel of cold heading | M5•120 |
| 30 | 16602 | Light spring washer | 4 | ø5 | |
| 31 | 212571600 | Stator | 1 | ||
| 32 | 70305 | Lock nut of hexagon flange faces | 2 | ||
| 33 | 212571700 | Rotor | 1 | ||
| 34 | 14032 | Bearing 6203-2Z | 2 |
FAQ
Q1: Are you factory or trade company?
A1: We are factory.
Q2: What the exactly address of your factory?
A2: Our factory is located in Linbei industrial area No.30 HangZhou City of ZHangZhoug Province, China
Q3: Warranty terms of your machine?
A3: Two years warranty for the machine and technical support according to your needs.
Q4: Will you provide some spare parts of the machines?
A4: Yes, of course.
Q5: How long will you take to arrange production?
A5: Generally, 1000 pcs can be delivered within 25 days
Q6: Can you accept OEM orders?
A6: Yes, with professional design team, OEM orders are highly welcome
Q7:Can you accept non-standard customization?
A7:We have the ability to develop new products and can customize, develop and research according to your requirements
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Remote Guided Maintenance |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 2 Years |
| Principle: | Mixed-Flow Compressor |
| Application: | Back Pressure Type, Intermediate Back Pressure Type, High Back Pressure Type, Low Back Pressure Type |
| Performance: | Low Noise, Variable Frequency, Explosion-Proof |
| Mute: | Mute |
| Samples: |
US$ 60/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How Are Vacuum Pumps Employed in the Production of Electronic Components?
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in the production of electronic components. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The production of electronic components often requires controlled environments with low or no atmospheric pressure. Vacuum pumps are employed in various stages of the production process to create and maintain these vacuum conditions. Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps are used in the production of electronic components:
1. Deposition Processes: Vacuum pumps are extensively used in deposition processes, such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD), which are commonly employed for thin film deposition on electronic components. These processes involve the deposition of materials onto substrates in a vacuum chamber. Vacuum pumps help create and maintain the necessary vacuum conditions required for precise and controlled deposition of the thin films.
2. Etching and Cleaning: Etching and cleaning processes are essential in the fabrication of electronic components. Vacuum pumps are used to create a vacuum environment in etching and cleaning chambers, where reactive gases or plasmas are employed to remove unwanted materials or residues from the surfaces of the components. The vacuum pumps help evacuate the chamber and ensure the efficient removal of byproducts and waste gases.
3. Drying and Bake-out: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the drying and bake-out processes of electronic components. After wet processes, such as cleaning or wet etching, components need to be dried thoroughly. Vacuum pumps help create a vacuum environment that facilitates the removal of moisture or solvents from the components, ensuring their dryness before subsequent processing steps. Additionally, vacuum bake-out is employed to remove moisture or other contaminants trapped within the components’ materials or structures, enhancing their reliability and performance.
4. Encapsulation and Packaging: Vacuum pumps are involved in the encapsulation and packaging stages of electronic component production. These processes often require the use of vacuum-sealed packaging to protect the components from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, or oxidation. Vacuum pumps assist in evacuating the packaging materials, creating a vacuum-sealed environment that helps maintain the integrity and longevity of the electronic components.
5. Testing and Quality Control: Vacuum pumps are utilized in testing and quality control processes for electronic components. Some types of testing, such as hermeticity testing, require the creation of a vacuum environment for evaluating the sealing integrity of electronic packages. Vacuum pumps help evacuate the testing chambers, ensuring accurate and reliable test results.
6. Soldering and Brazing: Vacuum pumps play a role in soldering and brazing processes for joining electronic components and assemblies. Vacuum soldering is a technique used to achieve high-quality solder joints by removing air and reducing the risk of voids, flux residuals, or oxidation. Vacuum pumps assist in evacuating the soldering chambers, creating the required vacuum conditions for precise and reliable soldering or brazing.
7. Surface Treatment: Vacuum pumps are employed in surface treatment processes for electronic components. These processes include plasma cleaning, surface activation, or surface modification techniques. Vacuum pumps help create the necessary vacuum environment where plasma or reactive gases are used to treat the component surfaces, improving adhesion, promoting bonding, or altering surface properties.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may be used in electronic component production, depending on the specific process requirements. Commonly used vacuum pump technologies include rotary vane pumps, turbo pumps, cryogenic pumps, and dry pumps.
In summary, vacuum pumps are essential in the production of electronic components, facilitating deposition processes, etching and cleaning operations, drying and bake-out stages, encapsulation and packaging, testing and quality control, soldering and brazing, as well as surface treatment. They enable the creation and maintenance of controlled vacuum environments, ensuring precise and reliable manufacturing processes for electronic components.

What Is the Difference Between Dry and Wet Vacuum Pumps?
Dry and wet vacuum pumps are two distinct types of pumps that differ in their operating principles and applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of the differences between them:
Dry Vacuum Pumps:
Dry vacuum pumps operate without the use of any lubricating fluid or sealing water in the pumping chamber. They rely on non-contact mechanisms to create a vacuum. Some common types of dry vacuum pumps include:
1. Rotary Vane Pumps: Rotary vane pumps consist of a rotor with vanes that slide in and out of slots in the rotor. The rotation of the rotor creates chambers that expand and contract, allowing the gas to be pumped. The vanes and the housing are designed to create a seal, preventing gas from flowing back into the pump. Rotary vane pumps are commonly used in laboratories, medical applications, and industrial processes where a medium vacuum level is required.
2. Dry Screw Pumps: Dry screw pumps use two or more intermeshing screws to compress and transport gas. As the screws rotate, the gas is trapped between the threads and transported from the suction side to the discharge side. Dry screw pumps are known for their high pumping speeds, low noise levels, and ability to handle various gases. They are used in applications such as semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing, and vacuum distillation.
3. Claw Pumps: Claw pumps use two rotors with claw-shaped lobes that rotate in opposite directions. The rotation creates a series of expanding and contracting chambers, enabling gas capture and pumping. Claw pumps are known for their oil-free operation, high pumping speeds, and suitability for handling dry and clean gases. They are commonly used in applications such as automotive manufacturing, food packaging, and environmental technology.
Wet Vacuum Pumps:
Wet vacuum pumps, also known as liquid ring pumps, operate by using a liquid, typically water, to create a seal and generate a vacuum. The liquid ring serves as both the sealing medium and the working fluid. Wet vacuum pumps are commonly used in applications where a higher level of vacuum is required or when handling corrosive gases. Some key features of wet vacuum pumps include:
1. Liquid Ring Pumps: Liquid ring pumps feature an impeller with blades that rotate eccentrically within a cylindrical casing. As the impeller rotates, the liquid forms a ring against the casing due to centrifugal force. The liquid ring creates a seal, and as the impeller spins, the volume of the gas chamber decreases, leading to the compression and discharge of gas. Liquid ring pumps are known for their ability to handle wet and corrosive gases, making them suitable for applications such as chemical processing, oil refining, and wastewater treatment.
2. Water Jet Pumps: Water jet pumps utilize a jet of high-velocity water to create a vacuum. The water jet entrains gases, and the mixture is then separated in a venturi section, where the water is recirculated, and the gases are discharged. Water jet pumps are commonly used in laboratories and applications where a moderate vacuum level is required.
The main differences between dry and wet vacuum pumps can be summarized as follows:
1. Operating Principle: Dry vacuum pumps operate without the need for any sealing fluid, while wet vacuum pumps utilize a liquid ring or water as a sealing and working medium.
2. Lubrication: Dry vacuum pumps do not require lubrication since there is no contact between moving parts, whereas wet vacuum pumps require the presence of a liquid for sealing and lubrication.
3. Applications: Dry vacuum pumps are suitable for applications where a medium vacuum level is required, and oil-free operation is desired. They are commonly used in laboratories, medical settings, and various industrial processes. Wet vacuum pumps, on the other hand, are used when a higher vacuum level is needed or when handling corrosive gases. They find applications in chemical processing, oil refining, and wastewater treatment, among others.
It’s important to note that the selection of a vacuum pump depends on specific requirements such as desired vacuum level, gas compatibility, operating conditions, and the nature of the application.
In summary, the primary distinction between dry and wet vacuum pumps lies in their operating principles, lubrication requirements, and applications. Dry vacuum pumps operate without any lubricating fluid, while wet vacuum pumps rely on a liquid ring or water for sealing and lubrication. The choice between dry and wet vacuum pumps depends on the specific needs of the application and the desired vacuum level.

What Is a Vacuum Pump, and How Does It Work?
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device used to create and maintain a vacuum or low-pressure environment within a closed system. Here’s a detailed explanation:
A vacuum pump operates on the principle of removing gas molecules from a sealed chamber, reducing the pressure inside the chamber to create a vacuum. The pump accomplishes this through various mechanisms and techniques, depending on the specific type of vacuum pump. Here are the basic steps involved in the operation of a vacuum pump:
1. Sealed Chamber:
The vacuum pump is connected to a sealed chamber or system from which air or gas molecules need to be evacuated. The chamber can be a container, a pipeline, or any other enclosed space.
2. Inlet and Outlet:
The vacuum pump has an inlet and an outlet. The inlet is connected to the sealed chamber, while the outlet may be vented to the atmosphere or connected to a collection system to capture or release the evacuated gas.
3. Mechanical Action:
The vacuum pump creates a mechanical action that removes gas molecules from the chamber. Different types of vacuum pumps use various mechanisms for this purpose:
– Positive Displacement Pumps: These pumps physically trap gas molecules and remove them from the chamber. Examples include rotary vane pumps, piston pumps, and diaphragm pumps.
– Momentum Transfer Pumps: These pumps use high-speed jets or rotating blades to transfer momentum to gas molecules, pushing them out of the chamber. Examples include turbomolecular pumps and diffusion pumps.
– Entrapment Pumps: These pumps capture gas molecules by adsorbing or condensing them on surfaces or in materials within the pump. Cryogenic pumps and ion pumps are examples of entrainment pumps.
4. Gas Evacuation:
As the vacuum pump operates, it creates a pressure differential between the chamber and the pump. This pressure differential causes gas molecules to move from the chamber to the pump’s inlet.
5. Exhaust or Collection:
Once the gas molecules are removed from the chamber, they are either exhausted into the atmosphere or collected and processed further, depending on the specific application.
6. Pressure Control:
Vacuum pumps often incorporate pressure control mechanisms to maintain the desired level of vacuum within the chamber. These mechanisms can include valves, regulators, or feedback systems that adjust the pump’s operation to achieve the desired pressure range.
7. Monitoring and Safety:
Vacuum pump systems may include sensors, gauges, or indicators to monitor the pressure levels, temperature, or other parameters. Safety features such as pressure relief valves or interlocks may also be included to protect the system and operators from overpressure or other hazardous conditions.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps have varying levels of vacuum they can achieve and are suitable for different pressure ranges and applications. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as the required vacuum level, gas composition, pumping speed, and the specific application’s requirements.
In summary, a vacuum pump is a device that removes gas molecules from a sealed chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. The pump accomplishes this through mechanical actions, such as positive displacement, momentum transfer, or entrapment. By creating a pressure differential, the pump evacuates gas from the chamber, and the gas is either exhausted or collected. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various industries, including manufacturing, research, and scientific applications.


editor by CX 2023-12-31
China Best Sales Rotary 50-100-190r/Min Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump with Motor Lrvp wholesaler
Product Description
COMPANY SHOW:
20 Years
ZiBoZhuoXin Pump Industry co,.Ltd is located in a century industrial city known as the Pump Capital of China—HangZhou city, ZheJiang Province. Has over 20 years’ experience of manufacturing vacuum pumps and 10+ years’ experience of exporting.
Various products
We can suppply all type of vacuum pumps and spare parts in China, 2BV/2BEA/2BEC/SK/2SK/JZJ2B/ etc, and other industrial machine;
24 Hours
Please do not hestiate to contact us if have any urgent matters,each of your inquiries will be taken into account and get our response within 24 hours.
Product Main feature:
Comparing with the SK, 2SK, SZ series water ring vacuum pumps, the 2BE series products are the ideal replacements pump due to its high vacuum, low power consumption, and steady running reliability.
By way of changing the structural material, it is also available in aspirating corrosive gas or with the corrosive liquid as the operating liquid.
Due to our high quality and competitive price , our pump are widely used for original CHINAMFG and CHINAMFG pump replacement in Mining industry, Electric power industry,petro chemical industry, pulp and paper industry,pharmaceutical industry,environment industry,food and beverage industry,Marine Industry and other general industry price
Due to its competitive price and higher performance, our pump is best choice for Siemens and some Italy pump replacement.
Welcome client from home and abroad to contact us for future cooperation.
performance : Siemens/Nash same
color : –
The main characteristics of 2BE1 series products:
2be water ring vacuum pump is a high efficiency and energy-saving product developed by our factory on the basis of many years of scientific research and production experience, combined with the advanced technology of imported products. It is usually used to pump gas without CHINAMFG particles, insoluble in water and corrosive, so as to form vacuum and pressure in closed container. By changing the structure material, it can also be used to suck corrosive gas or use corrosive liquid as working fluid. It is widely used in papermaking, chemical, petrochemical, light industry, pharmaceutical, food, metallurgy, building materials, stone tools, coal washing, mineral processing, chemical fertilizer and other industries.
Because in the working process, the pump compresses the gas in an isothermal state, so it can pump flammable and explosive gas. By changing the structural materials, it can also pump corrosive gas and use corrosive liquid as working fluid.
2be water ring vacuum pump adopts CHINAMFG and single action structure, which has the advantages of simple structure, convenient maintenance, reliable operation, high efficiency and energy saving. Compared with SK, 2SK and SZ series water ring vacuum pumps which are widely used in China, they have obvious advantages of high vacuum degree and low power consumption. They are ideal substitutes for SK water ring vacuum pumps, 2SK water ring vacuum pumps and SZ series water ring vacuum pumps. It can be used as the front stage pump and roots vacuum pump to form roots water ring vacuum unit, and 2 2be water ring pumps plus steam water separator, vacuum tank, heat exchanger, etc. can form a vacuum negative pressure station.
Mechanical seals (not compulsory) use best materials to prevent leakage when the pump works for quite long time.
(Example of 2BE1-152)
| Type | Speed (Drive type) r/min |
Shaft power kW |
Motor power kW |
Motor type |
Limited vacuum mbar |
Weight (Whole set) kg |
||
| Suction capacity | ||||||||
| m 3 /h | m 3 /min | |||||||
| 2BE1 151-0 | 1450(D) 1100(V) 1300(V) 1625(V) 1750(V) |
10.8 7.2 9.2 13.2 14.8 |
15 11 11 15 18.5 |
Y160L-4 Y160M-4 Y160M-4 Y160L-4 Y180M-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
405 300 360 445 470 |
6.8 5.0 6.0 7.4 7.8 |
469 428 444 469 503 |
| 2BE1 152-0 | 1450(D) 1100(V) 1300(V) 1625(V) 1750(V) |
12.5 8.3 10.5 15.0 17.2 |
15 11 15 18.5 22 |
Y160L-4 Y160M-4 Y160L-4 Y180M-4 Y180L-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
465 340 415 510 535 |
7.8 5.7 6.9 8.5 8.9 |
481 437 481 515 533 |
| 2BE1 153-0 | 1450(D) 1100(V) 1300(V) 1625(V) 1750(V) |
16.3 10.6 13.6 19.6 22.3 |
18.5 15 18.5 22 30 |
Y180M-4 Y160L-4 Y180M-4 Y180L-4 Y200L-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
600 445 540 660 700 |
10.0 7.4 9.0 11.0 11.7 |
533 480 533 551 601 |
| 2BE1 202-0 | 970(D) 790(V) 880(v) 1100(V) 1170(V) 1300(V) |
17 14 16 22 25 30 |
22 18.5 18.5 30 30 37 |
Y200L2-6 Y180M-4 Y180M-4 Y200L-4 Y200L-4 Y225S-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
760 590 670 850 890 950 |
12.7 9.8 11.2 14.2 14.8 15.8 |
875 850 850 940 945 995 |
| 2BE1 203-0 | 970(D) 790(V) 880(V) 1100(V) 1170(V) 1300(V) |
27 20 23 33 37 45 |
37 30 30 45 45 55 |
Y250M-6 Y200L-4 Y200L-4 Y225M-4 Y225M-4 Y250M-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
1120 880 1000 1270 1320 1400 |
18.7 14.7 16.7 21.2 22.0 23.3 |
1065 995 995 1080 1085 1170 |
| 2BE1 252-0 | 740(D) 558(V) 660(V) 832(V) 885(V) 938(V) |
38 26 31.8 49 54 60 |
45 30 37 55 75 75 |
Y280M-8 Y200L-4 Y225S-4 Y250M-4 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
1700 1200 1500 1850 2000 2100 |
28.3 20.0 25.0 30.8 33.3 35.0 |
1693 1460 1515 1645 1805 1805 |
| 2BE1 253-0 | 740(D) 560(V) 660(V) 740(V) 792(V) 833(V) 885(V) 938(V) |
54 37 45 54 60 68 77 86 |
75 45 55 75 75 90 90 110 |
Y315M-8 Y225M-4 Y250M-4 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
2450 1750 2140 2450 2560 2700 2870 3571 |
40.8 29.2 35.7 40.8 42.7 45.0 47.8 50.3 |
2215 1695 1785 1945 1945 2055 2060 2295 |
| 2BE1 303-0 | 740(D) 590(D) 466(V) 521(V) 583(V) 657(V) 743(V) |
98 65 48 54 64 78 99 |
110 75 55 75 75 90 132 |
Y315L2-8 Y315L2-10 Y250M-4 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y315M-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
4000 3200 2500 2800 3100 3580 4000 |
66.7 53.3 41.7 46.7 51.7 59.7 66.7 |
3200 3200 2645 2805 2810 2925 3290 |
| 2BE1 305-1 2BE1 306-1 |
740(D) 590(D) 490(V) 521(V) 583(V) 657(V) 743(V) |
102 70 55 59 68 84 103 |
132 90 75 75 90 110 132 |
Y355M1-8 Y355M1-10 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 Y315M-4 |
160mbar (-0.085MPa) |
4650 3750 3150 3320 3700 4130 4650 |
77.5 62.5 52.5 55.3 61.2 68.8 77.5 |
3800 3800 2950 3000 3100 3300 3450 |
| 2BE1 353-0 | 590(D) 390(V) 415(V) 464(V) 520(V) 585(V) 620(V) 660(V) |
121 65 70 81 97 121 133 152 |
160 75 90 110 132 160 160 185 |
Y355L2-10 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
5300 3580 3700 4100 4620 5200 5500 5850 |
88.3 59.7 61.7 68.3 77.0 86.7 91.7 97.5 |
4750 3560 3665 3905 4040 4100 4100 4240 |
| 2BE1 355-1 2BE1 356-1 |
590(D) 390(V) 435(V) 464(V) 520(V) 555(V) 585(V) 620(V) |
130 75 86 90 102 115 130 145 |
160 90 110 110 132 132 160 185 |
Y355L2-10 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 Y315S-4 Y315M-4 Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 |
160mbar (-0.085MPa) |
6200 4180 4600 4850 5450 5800 6100 6350 |
103.3 69.7 76.7 80.8 90.8 98.3 101.7 105.8 |
5000 3920 4150 4160 4290 4300 4350 4450 |
| 2BE1 403-0 | 330(V) 372(V) 420(V) 472(V) 530(V) 565(V) |
97 110 131 160 203 234 |
132 132 160 200 250 280 |
Y315M-4 Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 Y355M2-4 Y355L1-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
5160 5700 6470 7380 8100 8600 |
86.0 95.0 107.8 123.0 135.0 143.3 |
5860 5870 5950 6190 6630 6800 |
| 2BE1 405-1 2BE1 406-1 |
330(V) 372(V) 420(V) 472(V) 530(V) 565(V) |
100 118 140 170 206 235 |
132 160 185 200 250 280 |
Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 Y315L2-4 Y355M2-4 Y355L1-4 |
160mbar (-0.085MPa) |
6000 6700 7500 8350 9450 15710 |
100.0 111.7 125.0 139.2 157.5 168.3 |
5980 6070 6200 6310 6750 6920 |
More detail install drawing please contact Sales-in-Charge.
FAQ
Q: What’s your MOQ?
A: One set;
Q: What are the causes of no flow or insufficient flow of centrifugal pump?
A: There is air in the suction pipe or pump, which needs to be discharged. Air leakage is found in the suction pipeline, and the leakage is repaired. If the valve of suction line or discharge line is closed, relevant valve shall be opened. If the suction height is too high, recalculate the installation height. The suction line is too small or blocked.
Q: How to resist cavitation in centrifugal pump?
A: Improve the structure design from the suction to the impeller of the centrifugal pump;Adopt double stage suction impeller and use anti-cavitation material;
Q:What is the function of rubber ball in water ring vacuum pump?
A: Rubber ball in water ring vacuum pump, the correct name is called rubber ball valve. Its role is to eliminate the pump equipment in the operation process of the phenomenon of over compression or insufficient compression.
Q:How long is warranty?
A:One year formain construction warranty.
Q:How can I pay for my items? What is the payment you can provide
A:Usually by T/T, 30%-50% deposit payment once PI/Contract confirmed, then the remaining balance will be paid after inspection and before shipment via T/T or L/C;
Welcome client from home and abroad to contact us for future cooperation.
Detail size drawing and install drawing please contact our sales in charge to get;
Key:nash type/simense type/refurish/vacuum pumps/HangZhou CHINAMFG pump/;
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Reciprocating Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Positive Displacement Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Mainsuction Pump |
| Working Conditions: | Wet |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

How Are Vacuum Pumps Employed in the Production of Electronic Components?
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in the production of electronic components. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The production of electronic components often requires controlled environments with low or no atmospheric pressure. Vacuum pumps are employed in various stages of the production process to create and maintain these vacuum conditions. Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps are used in the production of electronic components:
1. Deposition Processes: Vacuum pumps are extensively used in deposition processes, such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD), which are commonly employed for thin film deposition on electronic components. These processes involve the deposition of materials onto substrates in a vacuum chamber. Vacuum pumps help create and maintain the necessary vacuum conditions required for precise and controlled deposition of the thin films.
2. Etching and Cleaning: Etching and cleaning processes are essential in the fabrication of electronic components. Vacuum pumps are used to create a vacuum environment in etching and cleaning chambers, where reactive gases or plasmas are employed to remove unwanted materials or residues from the surfaces of the components. The vacuum pumps help evacuate the chamber and ensure the efficient removal of byproducts and waste gases.
3. Drying and Bake-out: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the drying and bake-out processes of electronic components. After wet processes, such as cleaning or wet etching, components need to be dried thoroughly. Vacuum pumps help create a vacuum environment that facilitates the removal of moisture or solvents from the components, ensuring their dryness before subsequent processing steps. Additionally, vacuum bake-out is employed to remove moisture or other contaminants trapped within the components’ materials or structures, enhancing their reliability and performance.
4. Encapsulation and Packaging: Vacuum pumps are involved in the encapsulation and packaging stages of electronic component production. These processes often require the use of vacuum-sealed packaging to protect the components from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, or oxidation. Vacuum pumps assist in evacuating the packaging materials, creating a vacuum-sealed environment that helps maintain the integrity and longevity of the electronic components.
5. Testing and Quality Control: Vacuum pumps are utilized in testing and quality control processes for electronic components. Some types of testing, such as hermeticity testing, require the creation of a vacuum environment for evaluating the sealing integrity of electronic packages. Vacuum pumps help evacuate the testing chambers, ensuring accurate and reliable test results.
6. Soldering and Brazing: Vacuum pumps play a role in soldering and brazing processes for joining electronic components and assemblies. Vacuum soldering is a technique used to achieve high-quality solder joints by removing air and reducing the risk of voids, flux residuals, or oxidation. Vacuum pumps assist in evacuating the soldering chambers, creating the required vacuum conditions for precise and reliable soldering or brazing.
7. Surface Treatment: Vacuum pumps are employed in surface treatment processes for electronic components. These processes include plasma cleaning, surface activation, or surface modification techniques. Vacuum pumps help create the necessary vacuum environment where plasma or reactive gases are used to treat the component surfaces, improving adhesion, promoting bonding, or altering surface properties.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may be used in electronic component production, depending on the specific process requirements. Commonly used vacuum pump technologies include rotary vane pumps, turbo pumps, cryogenic pumps, and dry pumps.
In summary, vacuum pumps are essential in the production of electronic components, facilitating deposition processes, etching and cleaning operations, drying and bake-out stages, encapsulation and packaging, testing and quality control, soldering and brazing, as well as surface treatment. They enable the creation and maintenance of controlled vacuum environments, ensuring precise and reliable manufacturing processes for electronic components.

How Do Vacuum Pumps Affect the Performance of Vacuum Chambers?
When it comes to the performance of vacuum chambers, vacuum pumps play a critical role. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum chambers are enclosed spaces designed to create and maintain a low-pressure environment. They are used in various industries and scientific applications, such as manufacturing, research, and material processing. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate air and other gases from the chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure condition. The performance of vacuum chambers is directly influenced by the characteristics and operation of the vacuum pumps used.
Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps affect the performance of vacuum chambers:
1. Achieving and Maintaining Vacuum Levels: The primary function of vacuum pumps is to create and maintain the desired vacuum level within the chamber. Vacuum pumps remove air and other gases, reducing the pressure inside the chamber. The efficiency and capacity of the vacuum pump determine how quickly the desired vacuum level is achieved and how well it is maintained. High-performance vacuum pumps can rapidly evacuate the chamber and maintain the desired vacuum level even when there are gas leaks or continuous gas production within the chamber.
2. Pumping Speed: The pumping speed of a vacuum pump refers to the volume of gas it can remove from the chamber per unit of time. The pumping speed affects the rate at which the chamber can be evacuated and the time required to achieve the desired vacuum level. A higher pumping speed allows for faster evacuation and shorter cycle times, improving the overall efficiency of the vacuum chamber.
3. Ultimate Vacuum Level: The ultimate vacuum level is the lowest pressure that can be achieved in the chamber. It depends on the design and performance of the vacuum pump. Higher-quality vacuum pumps can achieve lower ultimate vacuum levels, which are important for applications requiring higher levels of vacuum or for processes that are sensitive to residual gases.
4. Leak Detection and Gas Removal: Vacuum pumps can also assist in leak detection and gas removal within the chamber. By continuously evacuating the chamber, any leaks or gas ingress can be identified and addressed promptly. This ensures that the chamber maintains the desired vacuum level and minimizes the presence of contaminants or unwanted gases.
5. Contamination Control: Some vacuum pumps, such as oil-sealed pumps, use lubricating fluids that can introduce contaminants into the chamber. These contaminants may be undesirable for certain applications, such as semiconductor manufacturing or research. Therefore, the choice of vacuum pump and its potential for introducing contaminants should be considered to maintain the required cleanliness and purity of the vacuum chamber.
6. Noise and Vibrations: Vacuum pumps can generate noise and vibrations during operation, which can impact the performance and usability of the vacuum chamber. Excessive noise or vibrations can interfere with delicate experiments, affect the accuracy of measurements, or cause mechanical stress on the chamber components. Selecting vacuum pumps with low noise and vibration levels is important for maintaining optimal chamber performance.
It’s important to note that the specific requirements and performance factors of a vacuum chamber can vary depending on the application. Different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, dry pumps, or turbomolecular pumps, offer varying capabilities and features that cater to specific needs. The choice of vacuum pump should consider factors such as the desired vacuum level, pumping speed, ultimate vacuum, contamination control, noise and vibration levels, and compatibility with the chamber materials and gases used.
In summary, vacuum pumps have a significant impact on the performance of vacuum chambers. They enable the creation and maintenance of the desired vacuum level, affect the pumping speed and ultimate vacuum achieved, assist in leak detection and gas removal, and influence contamination control. Careful consideration of the vacuum pump selection ensures optimal chamber performance for various applications.

What Is a Vacuum Pump, and How Does It Work?
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device used to create and maintain a vacuum or low-pressure environment within a closed system. Here’s a detailed explanation:
A vacuum pump operates on the principle of removing gas molecules from a sealed chamber, reducing the pressure inside the chamber to create a vacuum. The pump accomplishes this through various mechanisms and techniques, depending on the specific type of vacuum pump. Here are the basic steps involved in the operation of a vacuum pump:
1. Sealed Chamber:
The vacuum pump is connected to a sealed chamber or system from which air or gas molecules need to be evacuated. The chamber can be a container, a pipeline, or any other enclosed space.
2. Inlet and Outlet:
The vacuum pump has an inlet and an outlet. The inlet is connected to the sealed chamber, while the outlet may be vented to the atmosphere or connected to a collection system to capture or release the evacuated gas.
3. Mechanical Action:
The vacuum pump creates a mechanical action that removes gas molecules from the chamber. Different types of vacuum pumps use various mechanisms for this purpose:
– Positive Displacement Pumps: These pumps physically trap gas molecules and remove them from the chamber. Examples include rotary vane pumps, piston pumps, and diaphragm pumps.
– Momentum Transfer Pumps: These pumps use high-speed jets or rotating blades to transfer momentum to gas molecules, pushing them out of the chamber. Examples include turbomolecular pumps and diffusion pumps.
– Entrapment Pumps: These pumps capture gas molecules by adsorbing or condensing them on surfaces or in materials within the pump. Cryogenic pumps and ion pumps are examples of entrainment pumps.
4. Gas Evacuation:
As the vacuum pump operates, it creates a pressure differential between the chamber and the pump. This pressure differential causes gas molecules to move from the chamber to the pump’s inlet.
5. Exhaust or Collection:
Once the gas molecules are removed from the chamber, they are either exhausted into the atmosphere or collected and processed further, depending on the specific application.
6. Pressure Control:
Vacuum pumps often incorporate pressure control mechanisms to maintain the desired level of vacuum within the chamber. These mechanisms can include valves, regulators, or feedback systems that adjust the pump’s operation to achieve the desired pressure range.
7. Monitoring and Safety:
Vacuum pump systems may include sensors, gauges, or indicators to monitor the pressure levels, temperature, or other parameters. Safety features such as pressure relief valves or interlocks may also be included to protect the system and operators from overpressure or other hazardous conditions.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps have varying levels of vacuum they can achieve and are suitable for different pressure ranges and applications. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as the required vacuum level, gas composition, pumping speed, and the specific application’s requirements.
In summary, a vacuum pump is a device that removes gas molecules from a sealed chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. The pump accomplishes this through mechanical actions, such as positive displacement, momentum transfer, or entrapment. By creating a pressure differential, the pump evacuates gas from the chamber, and the gas is either exhausted or collected. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various industries, including manufacturing, research, and scientific applications.


editor by CX 2023-12-13
China supplier 5.5kw Oil Free IP54 Three Phase Electric Motor Ce Ring Air Blower Vacuum Pump vacuum pump ac system
Product Description
5.5kw Oil Free IP54 Three Phase Electric Motor Ring Blower vacuum pump
| Model | Stage/Phase | Frequency | Power | Voltage | Current | Airflow | Vacuum | Pressure | Noise | weight |
| Hz | KW | V | A | m3/h | mbar | mbar | db | KG | ||
| 2JM 810 H27 | Single/Three | 50 | 7.5 | 345-415△/600-720Y | 16.7△/9.6Y | 530 | -320 | 430 | 70 | 66 |
| 60 | 8.6 | 380-480△/660-720Y | 17.3△/10.0Y | 620 | -350 | 400 | 74 |
Other main product At 50Hz ( voltage can customize )
Application:
- Agriculture(Fish pond and aeration tanks)
- Beverage(bottle drying)
- Bio fuels/bio-gas system
- Food and vegetable processing
- Medical and Health service(Dental cart and dental vacuum)
- Package (Air knives blown-off / Labeling/Drying)
- Plastics/Rubber(Air knives blown-off/ Bottle blow moulding/ Extruder Degassing/Pneumatic conveying/ Thermoforming)
- Printing
- Paper and pulp/ paper converting
- Textile industry
- Transportation/Loading/Unloading(Pneumatic conveying/material handling)
- Water treatment/sewage treatment
- Woodworking(CNC Routing/bulk handling
Air Blowers Export Service:
18 months warranty
Professional engineer will help to recommend the most suitable models
after studying customers’ requirements,
OEM service available.
24 hours service online,you can touch us by email, , ,
7 days delivery time and safe shipment
Contact
| Material: | Aluminum |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Aeration |
| Flow Direction: | Centrifugal |
| Pressure: | High Pressure |
| Certification: | CE, CCC |
| Power: | 7.5kw |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in the Aerospace Sector?
Vacuum pumps indeed have various applications in the aerospace sector. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in several areas of the aerospace industry, supporting various processes and systems. Some of the key applications of vacuum pumps in the aerospace sector include:
1. Space Simulation Chambers: Vacuum pumps are used in space simulation chambers to replicate the low-pressure conditions experienced in outer space. These chambers are utilized for testing and validating the performance and functionality of aerospace components and systems under simulated space conditions. Vacuum pumps create and maintain the necessary vacuum environment within these chambers, allowing engineers and scientists to evaluate the behavior and response of aerospace equipment in space-like conditions.
2. Propellant Management: In space propulsion systems, vacuum pumps are employed for propellant management. They help in the transfer, circulation, and pressurization of propellants, such as liquid rocket fuels or cryogenic fluids, in both launch vehicles and spacecraft. Vacuum pumps assist in creating the required pressure differentials for propellant flow and control, ensuring efficient and reliable operation of propulsion systems.
3. Environmental Control Systems: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the environmental control systems of aircraft and spacecraft. These systems are responsible for maintaining the desired atmospheric conditions, including temperature, humidity, and cabin pressure, to ensure the comfort, safety, and well-being of crew members and passengers. Vacuum pumps are used to regulate and control the cabin pressure, facilitating the circulation of fresh air and maintaining the desired air quality within the aircraft or spacecraft.
4. Satellite Technology: Vacuum pumps find numerous applications in satellite technology. They are used in the fabrication and testing of satellite components, such as sensors, detectors, and electronic devices. Vacuum pumps help create the necessary vacuum conditions for thin film deposition, surface treatment, and testing processes, ensuring the performance and reliability of satellite equipment. Additionally, vacuum pumps are employed in satellite propulsion systems to manage propellants and provide thrust for orbital maneuvers.
5. Avionics and Instrumentation: Vacuum pumps are involved in the production and testing of avionics and instrumentation systems used in aerospace applications. They facilitate processes such as thin film deposition, vacuum encapsulation, and vacuum drying, ensuring the integrity and functionality of electronic components and circuitry. Vacuum pumps are also utilized in vacuum leak testing, where they help create a vacuum environment to detect and locate any leaks in aerospace systems and components.
6. High Altitude Testing: Vacuum pumps are used in high altitude testing facilities to simulate the low-pressure conditions encountered at high altitudes. These testing facilities are employed for evaluating the performance and functionality of aerospace equipment, such as engines, materials, and structures, under simulated high altitude conditions. Vacuum pumps create and control the required low-pressure environment, allowing engineers and researchers to assess the behavior and response of aerospace systems in high altitude scenarios.
7. Rocket Engine Testing: Vacuum pumps are crucial in rocket engine testing facilities. They are utilized to evacuate and maintain the vacuum conditions in engine test chambers or nozzles during rocket engine testing. By creating a vacuum environment, these pumps simulate the conditions experienced by rocket engines in the vacuum of space, enabling accurate testing and evaluation of engine performance, thrust levels, and efficiency.
It’s important to note that aerospace applications often require specialized vacuum pumps capable of meeting stringent requirements, such as high reliability, low outgassing, compatibility with propellants or cryogenic fluids, and resistance to extreme temperatures and pressures.
In summary, vacuum pumps are extensively used in the aerospace sector for a wide range of applications, including space simulation chambers, propellant management, environmental control systems, satellite technology, avionics and instrumentation, high altitude testing, and rocket engine testing. They contribute to the development, testing, and operation of aerospace equipment, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and safety.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used for Leak Detection?
Yes, vacuum pumps can be used for leak detection purposes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Leak detection is a critical task in various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and HVAC. It involves identifying and locating leaks in a system or component that may result in the loss of fluids, gases, or pressure. Vacuum pumps can play a significant role in leak detection processes by creating a low-pressure environment and facilitating the detection of leaks through various methods.
Here are some ways in which vacuum pumps can be used for leak detection:
1. Vacuum Decay Method: The vacuum decay method is a common technique used for leak detection. It involves creating a vacuum in a sealed system or component using a vacuum pump and monitoring the pressure change over time. If there is a leak present, the pressure will gradually increase due to the ingress of air or gas. By measuring the rate of pressure rise, the location and size of the leak can be estimated. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate the system and establish the initial vacuum required for the test.
2. Bubble Testing: Bubble testing is a simple and visual method for detecting leaks. In this method, the component or system being tested is pressurized with a gas, and then immersed in a liquid, typically soapy water. If there is a leak, the gas escaping from the component will form bubbles in the liquid, indicating the presence and location of the leak. Vacuum pumps can be used to create a pressure differential that forces gas out of the leak, making it easier to detect the bubbles.
3. Helium Leak Detection: Helium leak detection is a highly sensitive method used to locate extremely small leaks. Helium, being a small atom, can easily penetrate small openings and leaks. In this method, the system or component is pressurized with helium gas, and a vacuum pump is used to evacuate the surrounding area. A helium leak detector is then used to sniff or scan the area for the presence of helium, indicating the location of the leak. Vacuum pumps are essential for creating the low-pressure environment required for this method and ensuring accurate detection.
4. Pressure Change Testing: Vacuum pumps can also be used in pressure change testing for leak detection. This method involves pressurizing a system or component and then isolating it from the pressure source. The pressure is monitored over time, and any significant pressure drop indicates the presence of a leak. Vacuum pumps can be used to evacuate the system after pressurization, returning it to atmospheric pressure for comparison or retesting.
5. Mass Spectrometer Leak Detection: Mass spectrometer leak detection is a highly sensitive and precise method used to identify and quantify leaks. It involves introducing a tracer gas, usually helium, into the system or component being tested. A vacuum pump is used to evacuate the surrounding area, and a mass spectrometer is employed to analyze the gas samples for the presence of the tracer gas. This method allows for accurate detection and quantification of leaks down to very low levels. Vacuum pumps are crucial for creating the necessary vacuum conditions and ensuring reliable results.
In summary, vacuum pumps can be effectively used for leak detection purposes. They facilitate various leak detection methods such as vacuum decay, bubble testing, helium leak detection, pressure change testing, and mass spectrometer leak detection. Vacuum pumps create the required low-pressure environment, assist in evacuating the system or component being tested, and enable accurate and reliable leak detection. The choice of vacuum pump depends on the specific requirements of the leak detection method and the sensitivity needed for the application.

What Are the Primary Applications of Vacuum Pumps?
Vacuum pumps have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Industrial Processes:
Vacuum pumps play a vital role in numerous industrial processes, including:
– Vacuum Distillation: Vacuum pumps are used in distillation processes to lower the boiling points of substances, enabling separation and purification of various chemicals and compounds.
– Vacuum Drying: Vacuum pumps aid in drying processes by creating a low-pressure environment, which accelerates moisture removal from materials without excessive heat.
– Vacuum Packaging: Vacuum pumps are used in the food industry to remove air from packaging containers, prolonging the shelf life of perishable goods by reducing oxygen exposure.
– Vacuum Filtration: Filtration processes can benefit from vacuum pumps to enhance filtration rates by applying suction, facilitating faster separation of solids and liquids.
2. Laboratory and Research:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories and research facilities for various applications:
– Vacuum Chambers: Vacuum pumps create controlled low-pressure environments within chambers for conducting experiments, testing materials, or simulating specific conditions.
– Mass Spectrometry: Mass spectrometers often utilize vacuum pumps to create the necessary vacuum conditions for ionization and analysis of samples.
– Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps enable freeze-drying processes, where samples are frozen and then subjected to a vacuum, allowing the frozen water to sublimate directly from solid to vapor state.
– Electron Microscopy: Vacuum pumps are essential for electron microscopy techniques, providing the necessary vacuum environment for high-resolution imaging of samples.
3. Semiconductor and Electronics Industries:
High vacuum pumps are critical in the semiconductor and electronics industries for manufacturing and testing processes:
– Semiconductor Fabrication: Vacuum pumps are used in various stages of chip manufacturing, including deposition, etching, and ion implantation processes.
– Thin Film Deposition: Vacuum pumps create the required vacuum conditions for depositing thin films of materials onto substrates, as done in the production of solar panels, optical coatings, and electronic components.
– Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are utilized in leak testing applications to detect and locate leaks in electronic components, systems, or pipelines.
4. Medical and Healthcare:
Vacuum pumps have several applications in the medical and healthcare sectors:
– Vacuum Assisted Wound Closure: Vacuum pumps are used in negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), where they create a controlled vacuum environment to promote wound healing and removal of excess fluids.
– Laboratory Equipment: Vacuum pumps are essential in medical and scientific equipment such as vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, and centrifugal concentrators.
– Anesthesia and Medical Suction: Vacuum pumps are utilized in anesthesia machines and medical suction devices to create suction and remove fluids or gases from the patient’s body.
5. HVAC and Refrigeration:
Vacuum pumps are employed in the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries:
– Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems: Vacuum pumps are used during system installation, maintenance, and repair to evacuate moisture and air from refrigeration and air conditioning systems, ensuring efficient operation.
– Vacuum Insulation Panels: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the manufacturing of vacuum insulation panels, which offer superior insulation properties for buildings and appliances.
6. Power Generation:
Vacuum pumps play a role in power generation applications:
– Steam Condenser Systems: Vacuum pumps are used in power plants to remove non-condensable gases from steam condenser systems, improving thermal efficiency.
– Gas Capture: Vacuum pumps are utilized to capture and remove gases, such as hydrogen or helium, in nuclear power plants, research reactors, or particle accelerators.
These are just a few examples of the primary applications of vacuum pumps. The versatility and wide range of vacuum pump types make them essential in numerous industries, contributing to various manufacturing processes, research endeavors, and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2023-11-20
China best Wholesale Xgb-4000 Copper Motor Machine 380V Peripheral Vacuum Pump for Agriculture and Restaurant with Hot selling
Product Description
Wholesale XGB-4000 Copper Motor Machine 380V Peripheral Vacuum Pump For Agriculture And Restaurant
Our Services
· Customizing the fans according to customers’ requirements.
· Delivery time for sample order: 1-5 days, for pallets order 7-20 days after receiving clear payment
· Warranty: 1 year for repairing or replacement of fans, customs duty & freight not included
FAQ
Q: How To Order ?
A: Step 1, please tell us what model and quantity you need;
Step 2, then we will make a PI for you to confirm the order details;
Step 3, when we confirmed everything, can arrange the payment;
Step 4, finally we deliver the goods within the stipulated time.
Q: What is the MOQ?
R: 100 pieces, accept sample.
Q: When you ship my order
R: Normally container need 15-40days, sample 3-7DAYS
Q: How about the quality guarantee period?
R: One year.
Q: Do you have the certificates?
R: Yes, we have passed the CE and CCC certification.
Q: Do you offer ODM & OEM service.
R: Yes, we can custom design for specific application.
Q: When can I get the quotation?
R:We usually quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry. If you are urgent to get the price, please send the message on trade management or call us directly.
Q: How can I get a sample to check your quality?
R:After price confirmed, you can require for samples to check quality.
If you need the samples, we will charge for the sample cost. But the sample cost can be refundable when your quantity of first order is above the MOQ
Q: What is your main market?
R:Southeast Asia, South America,Middle East.North America,EU
After-sales Service
1 year warranty for all kinds of products;
If you find any defective accessories first time, we will give you the new parts for free to replace in the next order, as an experienced manufacturer, you can rest assured of the quality and after-sales service.
Established in 1998,DET motor is a professional manufacturer and exporter that is concerned with the design, development and production of motors. We are located in ZheJiang city, with convenient transportation access. All of our products comply with international quality standards and are greatly appreciated in a variety of different markets throughout the world.
We have over 550 employees, an annual sales figure that exceeds USD300,000,000 and are currently exporting 50% of our production worldwide. Our well-equipped facilities and excellent quality control throughout all stages of production enables us to guarantee total customer satisfaction.
As a result of our high quality products and outstanding customer service, we have gained a global sales network CHINAMFG European.
If you are interested in any of our products or would like to discuss a custom order, please feel free to contact us. We are looking CHINAMFG to forming successful business relationships with new clients around the world in the near future.
| Transfer | FOB/CIF |
| Payment | TT/LC/VISA/MASTER |
| Port | ZheJiang /HangZhou/HangZhou/HangZhou |
| After-sales Service: | Online |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
| Structure: | Rotary Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Entrapment Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Samples: |
US$ 240/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used for Vacuum Furnaces?
Yes, vacuum pumps can be used for vacuum furnaces. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum furnaces are specialized heating systems used in various industries for heat treatment processes that require controlled environments with low or no atmospheric pressure. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in creating and maintaining the vacuum conditions necessary for the operation of vacuum furnaces.
Here are some key points regarding the use of vacuum pumps in vacuum furnaces:
1. Vacuum Creation: Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate the furnace chamber, creating a low-pressure or near-vacuum environment. This is essential for the heat treatment processes carried out in the furnace, as it helps eliminate oxygen and other reactive gases, preventing oxidation or unwanted chemical reactions with the heated materials.
2. Pressure Control: Vacuum pumps provide the means to control and maintain the desired pressure levels within the furnace chamber during the heat treatment process. Precise pressure control is necessary to achieve the desired metallurgical and material property changes during processes such as annealing, brazing, sintering, and hardening.
3. Contamination Prevention: By removing gases and impurities from the furnace chamber, vacuum pumps help prevent contamination of the heated materials. This is particularly important in applications where cleanliness and purity of the processed materials are critical, such as in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
4. Rapid Cooling: Some vacuum furnace systems incorporate rapid cooling capabilities, known as quenching. Vacuum pumps assist in facilitating the rapid cooling process by removing the heat generated during quenching, ensuring efficient cooling and minimizing distortion or other unwanted effects on the treated materials.
5. Process Flexibility: Vacuum pumps provide flexibility in the type of heat treatment processes that can be performed in vacuum furnaces. Different heat treatment techniques, such as vacuum annealing, vacuum brazing, or vacuum carburizing, require specific pressure levels and atmospheric conditions that can be achieved and maintained with the use of vacuum pumps.
6. Vacuum Pump Types: Different types of vacuum pumps can be used in vacuum furnaces, depending on the specific requirements of the heat treatment process. Commonly used vacuum pump technologies include oil-sealed rotary vane pumps, dry screw pumps, diffusion pumps, and cryogenic pumps. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as required vacuum level, pumping speed, reliability, and compatibility with the process gases.
7. Maintenance and Monitoring: Proper maintenance and monitoring of vacuum pumps are essential to ensure their optimal performance and reliability. Regular inspections, lubrication, and replacement of consumables (such as oil or filters) are necessary to maintain the efficiency and longevity of the vacuum pump system.
8. Safety Considerations: Operating vacuum furnaces with vacuum pumps requires adherence to safety protocols. This includes proper handling of potentially hazardous gases or chemicals used in the heat treatment processes, as well as following safety guidelines for operating and maintaining the vacuum pump system.
Overall, vacuum pumps are integral components of vacuum furnaces, enabling the creation and maintenance of the required vacuum conditions for precise and controlled heat treatment processes. They contribute to the quality, consistency, and efficiency of the heat treatment operations performed in vacuum furnaces across a wide range of industries.

What Is the Difference Between Dry and Wet Vacuum Pumps?
Dry and wet vacuum pumps are two distinct types of pumps that differ in their operating principles and applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of the differences between them:
Dry Vacuum Pumps:
Dry vacuum pumps operate without the use of any lubricating fluid or sealing water in the pumping chamber. They rely on non-contact mechanisms to create a vacuum. Some common types of dry vacuum pumps include:
1. Rotary Vane Pumps: Rotary vane pumps consist of a rotor with vanes that slide in and out of slots in the rotor. The rotation of the rotor creates chambers that expand and contract, allowing the gas to be pumped. The vanes and the housing are designed to create a seal, preventing gas from flowing back into the pump. Rotary vane pumps are commonly used in laboratories, medical applications, and industrial processes where a medium vacuum level is required.
2. Dry Screw Pumps: Dry screw pumps use two or more intermeshing screws to compress and transport gas. As the screws rotate, the gas is trapped between the threads and transported from the suction side to the discharge side. Dry screw pumps are known for their high pumping speeds, low noise levels, and ability to handle various gases. They are used in applications such as semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing, and vacuum distillation.
3. Claw Pumps: Claw pumps use two rotors with claw-shaped lobes that rotate in opposite directions. The rotation creates a series of expanding and contracting chambers, enabling gas capture and pumping. Claw pumps are known for their oil-free operation, high pumping speeds, and suitability for handling dry and clean gases. They are commonly used in applications such as automotive manufacturing, food packaging, and environmental technology.
Wet Vacuum Pumps:
Wet vacuum pumps, also known as liquid ring pumps, operate by using a liquid, typically water, to create a seal and generate a vacuum. The liquid ring serves as both the sealing medium and the working fluid. Wet vacuum pumps are commonly used in applications where a higher level of vacuum is required or when handling corrosive gases. Some key features of wet vacuum pumps include:
1. Liquid Ring Pumps: Liquid ring pumps feature an impeller with blades that rotate eccentrically within a cylindrical casing. As the impeller rotates, the liquid forms a ring against the casing due to centrifugal force. The liquid ring creates a seal, and as the impeller spins, the volume of the gas chamber decreases, leading to the compression and discharge of gas. Liquid ring pumps are known for their ability to handle wet and corrosive gases, making them suitable for applications such as chemical processing, oil refining, and wastewater treatment.
2. Water Jet Pumps: Water jet pumps utilize a jet of high-velocity water to create a vacuum. The water jet entrains gases, and the mixture is then separated in a venturi section, where the water is recirculated, and the gases are discharged. Water jet pumps are commonly used in laboratories and applications where a moderate vacuum level is required.
The main differences between dry and wet vacuum pumps can be summarized as follows:
1. Operating Principle: Dry vacuum pumps operate without the need for any sealing fluid, while wet vacuum pumps utilize a liquid ring or water as a sealing and working medium.
2. Lubrication: Dry vacuum pumps do not require lubrication since there is no contact between moving parts, whereas wet vacuum pumps require the presence of a liquid for sealing and lubrication.
3. Applications: Dry vacuum pumps are suitable for applications where a medium vacuum level is required, and oil-free operation is desired. They are commonly used in laboratories, medical settings, and various industrial processes. Wet vacuum pumps, on the other hand, are used when a higher vacuum level is needed or when handling corrosive gases. They find applications in chemical processing, oil refining, and wastewater treatment, among others.
It’s important to note that the selection of a vacuum pump depends on specific requirements such as desired vacuum level, gas compatibility, operating conditions, and the nature of the application.
In summary, the primary distinction between dry and wet vacuum pumps lies in their operating principles, lubrication requirements, and applications. Dry vacuum pumps operate without any lubricating fluid, while wet vacuum pumps rely on a liquid ring or water for sealing and lubrication. The choice between dry and wet vacuum pumps depends on the specific needs of the application and the desired vacuum level.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in Laboratories?
Yes, vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories for a wide range of applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are essential tools in laboratory settings as they enable scientists and researchers to create and control vacuum or low-pressure environments. These controlled conditions are crucial for various scientific processes and experiments. Here are some key reasons why vacuum pumps are used in laboratories:
1. Evaporation and Distillation: Vacuum pumps are frequently used in laboratory evaporation and distillation processes. By creating a vacuum, they lower the boiling point of liquids, allowing for gentler and more controlled evaporation. This is particularly useful for heat-sensitive substances or when precise control over the evaporation process is required.
2. Filtration: Vacuum filtration is a common technique in laboratories for separating solids from liquids or gases. Vacuum pumps create suction, which helps draw the liquid or gas through the filter, leaving the solid particles behind. This method is widely used in processes such as sample preparation, microbiology, and analytical chemistry.
3. Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in freeze drying or lyophilization processes. Freeze drying involves removing moisture from a substance while it is in a frozen state, preserving its structure and properties. Vacuum pumps facilitate the sublimation of frozen water directly into vapor, resulting in the removal of moisture under low-pressure conditions.
4. Vacuum Ovens and Chambers: Vacuum pumps are used in conjunction with vacuum ovens and chambers to create controlled low-pressure environments for various applications. Vacuum ovens are used for drying heat-sensitive materials, removing solvents, or conducting reactions under reduced pressure. Vacuum chambers are utilized for testing components under simulated space or high-altitude conditions, degassing materials, or studying vacuum-related phenomena.
5. Analytical Instruments: Many laboratory analytical instruments rely on vacuum pumps to function properly. For example, mass spectrometers, electron microscopes, surface analysis equipment, and other analytical instruments often require vacuum conditions to maintain sample integrity and achieve accurate results.
6. Chemistry and Material Science: Vacuum pumps are employed in numerous chemical and material science experiments. They are used for degassing samples, creating controlled atmospheres, conducting reactions under reduced pressure, or studying gas-phase reactions. Vacuum pumps are also used in thin film deposition techniques like physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
7. Vacuum Systems for Experiments: In scientific research, vacuum systems are often designed and constructed for specific experiments or applications. These systems can include multiple vacuum pumps, valves, and chambers to create specialized vacuum environments tailored to the requirements of the experiment.
Overall, vacuum pumps are versatile tools that find extensive use in laboratories across various scientific disciplines. They enable researchers to control and manipulate vacuum or low-pressure conditions, facilitating a wide range of processes, experiments, and analyses. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as required vacuum level, flow rate, chemical compatibility, and specific application needs.


editor by CX 2023-11-17
China manufacturer CHINAMFG High Quality Auto Parts Engine Motor Vacuum Pump for Mercede W251 R350 SL400 Cl550 Cls63 Amg 2762300165 vacuum pump design
Product Description
| Product Information | |
| Product name | Vacuum Pump |
| OEM | 27623 |
| Warranty | 1 year |
| Certifications | CE |
| Condition | Brand-new |
| Appliction | For Mercede W251 R350 SL400 CL550 CLS63 AMG |
| Brand Name | ZOOMKEY |
| Place of Origin | ZheJiang , China |
| Quality | High-performance |
| Related Products |
| Company Profile |
| Our advantages |
One-stop solution for auto parts
ODM and OEM customized
with 12 months-24 months warranty
high quality, professional service
Zoomrich is a company specialized in distribution and service for CHINAMFG car parts,Especially in Volkswagen, Audi, Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Por sche,Jaguar,Land-Rover autoparts.Our business includes temperature control system,suspension parts, engine parts, electrical parts, and some other product lines.We are based in ZheJiang , and cooperate with many international first-line brands in order to meet the customer’s choice of diversity. Based on 12 years of experience,We accumulated a lot of factory resources and build a long-term cooperation in China which include OEM factory,OES resources,IAM factory verified by International famous brand.
About Us
Zhongyu electronic commerce(ZheJiang )Co.Ltd.is specialized in serving the German car system. The products are suitable for Mercedes-Benz, BMW,Volkswagen imported and other luxury cars. It covers auto engine system, auto transmission system, auto covering system, auto temperature control system,auto suspension and steering system, auto electronic system and so on.
With years of experience in the market of China in auto parts field ,our products have been exported to all over the world simultaneously.We have integrate the R&D,manufacture and trade. Supportina ODM
&OEM customized,and strict support confidentiality of customer brands and property rights. We will try our best to cooperation with you to establish a CHINAMFG relationship.
| AFQ |
1. who are we?
We are based in ZheJiang , China, start from 2017,sell to Western Europe(20.00%),Domestic Market(20.00%),North America(10.00%),South America(10.00%),Eastern Europe(10.00%),Northern Europe(10.00%),Southeast Asia(5.00%),Africa(5.00%),Mid East(5.00%),Eastern Asia(5.00%). There are total about 11-50 people in our office.
2. how can we guarantee quality?
Always a pre-production sample before mass production;
Always final Inspection before shipment;
3.what can you buy from us?
camshaft adjuster,headlamp accessories,cylinder head cover,shock absorber,tensioner
4. why should you buy from us not from other suppliers?
One-stop solution for auto parts ODM and OEM customized with 12 months-24 months warranty
5. what services can we provide?
Accepted Delivery Terms: FOB,CFR,CIF,EXW,Express Delivery;
Accepted Payment Currency:USD,EUR,CNY;
Accepted Payment Type: T/T,L/C,D/P D/A,MoneyGram,PayPal,Western Union,Cash;
Language Spoken:English,Chinese
| After-sales Service: | 12 Months |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Product Name: | Vacuum Pump |
| Appliction: | for Mercede W251 R350 SL400 Cl550 Cls63 Amg |
| Package: | Carton Box |
| Quality: | High-Performance |
| Samples: |
US$ 33/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used for Vacuum Packaging?
Yes, vacuum pumps can be used for vacuum packaging. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum packaging is a method used to remove air from a package or container, creating a vacuum environment. This process helps to extend the shelf life of perishable products, prevent spoilage, and maintain product freshness. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in achieving the desired vacuum level for effective packaging.
When it comes to vacuum packaging, there are primarily two types of vacuum pumps commonly used:
1. Single-Stage Vacuum Pumps: Single-stage vacuum pumps are commonly used for vacuum packaging applications. These pumps use a single rotating vane or piston to create a vacuum. They can achieve moderate vacuum levels suitable for most packaging requirements. Single-stage pumps are relatively simple in design, compact, and cost-effective.
2. Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps: Rotary vane vacuum pumps are another popular choice for vacuum packaging. These pumps utilize multiple vanes mounted on a rotor to create a vacuum. They offer higher vacuum levels compared to single-stage pumps, making them suitable for applications that require deeper levels of vacuum. Rotary vane pumps are known for their reliability, consistent performance, and durability.
When using vacuum pumps for vacuum packaging, the following steps are typically involved:
1. Preparation: Ensure that the packaging material, such as vacuum bags or containers, is suitable for vacuum packaging and can withstand the vacuum pressure without leakage. Place the product to be packaged inside the appropriate packaging material.
2. Sealing: Properly seal the packaging material, either by heat sealing or using specialized vacuum sealing equipment. This ensures an airtight enclosure for the product.
3. Vacuum Pump Operation: Connect the vacuum pump to the packaging equipment or directly to the packaging material. Start the vacuum pump to initiate the vacuuming process. The pump will remove the air from the packaging, creating a vacuum environment.
4. Vacuum Level Control: Monitor the vacuum level during the packaging process using pressure gauges or vacuum sensors. Depending on the specific packaging requirements, adjust the vacuum level accordingly. The goal is to achieve the desired vacuum level suitable for the product being packaged.
5. Sealing and Closure: Once the desired vacuum level is reached, seal the packaging material completely to maintain the vacuum environment. This can be done by heat sealing the packaging material or using specialized sealing mechanisms designed for vacuum packaging.
6. Product Labeling and Storage: After sealing, label the packaged product as necessary and store it appropriately, considering factors such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure, to maximize product shelf life.
It’s important to note that the specific vacuum level required for vacuum packaging may vary depending on the product being packaged. Some products may require a partial vacuum, while others may require a more stringent vacuum level. The choice of vacuum pump and the control mechanisms employed will depend on the specific vacuum packaging requirements.
Vacuum pumps are widely used in various industries for vacuum packaging applications, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and more. They provide an efficient and reliable means of creating a vacuum environment, helping to preserve product quality and extend shelf life.

How Do Vacuum Pumps Impact the Quality of 3D Printing?
Vacuum pumps play a significant role in improving the quality and performance of 3D printing processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by depositing successive layers of material. Vacuum pumps are utilized in various aspects of 3D printing to enhance the overall quality, accuracy, and reliability of printed parts. Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps impact 3D printing:
1. Material Handling and Filtration: Vacuum pumps are used in 3D printing systems to handle and control the flow of materials. They create the necessary suction force to transport powdered materials, such as polymers or metal powders, from storage containers to the printing chamber. Vacuum systems also assist in filtering and removing unwanted particles or impurities from the material, ensuring the purity and consistency of the feedstock. This helps to prevent clogging or contamination issues during the printing process.
2. Build Plate Adhesion: Proper adhesion of the printed object to the build plate is crucial for achieving dimensional accuracy and preventing warping or detachment during the printing process. Vacuum pumps are employed to create a vacuum environment or suction force that securely holds the build plate and ensures firm adhesion between the first layer of the printed object and the build surface. This promotes stability and minimizes the risk of layer shifting or deformation during the printing process.
3. Material Drying: Many 3D printing materials, such as filament or powdered polymers, can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment. Moisture-contaminated materials can lead to poor print quality, reduced mechanical properties, or defects in the printed parts. Vacuum pumps with integrated drying capabilities can be employed to create a low-pressure environment, effectively removing moisture from the materials before they are used in the printing process. This ensures the dryness and quality of the materials, resulting in improved print outcomes.
4. Resin Handling in Stereolithography (SLA): In SLA 3D printing, a liquid resin is selectively cured using light sources to create the desired object. Vacuum pumps are utilized to facilitate the resin handling process. They can be employed to degas or remove air bubbles from the liquid resin, ensuring a smooth and bubble-free flow during material dispensing. This helps to prevent defects and imperfections caused by trapped air or bubbles in the final printed part.
5. Enclosure Pressure Control: Some 3D printing processes, such as selective laser sintering (SLS) or binder jetting, require the printing chamber to be maintained at a specific pressure or controlled atmosphere. Vacuum pumps are used to create a controlled low-pressure or vacuum environment within the printing chamber, enabling precise pressure regulation and maintaining the desired conditions for optimal printing results. This control over the printing environment helps to prevent oxidation, improve material flow, and enhance the quality and consistency of printed parts.
6. Post-Processing and Cleaning: Vacuum pumps can also aid in post-processing steps and cleaning of 3D printed parts. For instance, in processes like support material removal or surface finishing, vacuum systems can assist in the removal of residual support structures or excess powder from printed objects. They can also be employed in vacuum-based cleaning methods, such as vapor smoothing, to achieve smoother surface finishes and enhance the aesthetics of the printed parts.
7. System Maintenance and Filtration: Vacuum pumps used in 3D printing systems require regular maintenance and proper filtration to ensure their efficient and reliable operation. Effective filtration systems within the vacuum pumps help to remove any contaminants or particles generated during printing, preventing their circulation and potential deposition on the printed parts. This helps to maintain the cleanliness of the printing environment and minimize the risk of defects or impurities in the final printed objects.
In summary, vacuum pumps have a significant impact on the quality of 3D printing. They contribute to material handling and filtration, build plate adhesion, material drying, resin handling in SLA, enclosure pressure control, post-processing and cleaning, as well as system maintenance and filtration. By utilizing vacuum pumps in these critical areas, 3D printing processes can achieve improved accuracy, dimensional stability, material quality, and overall print quality.

How Do You Choose the Right Size Vacuum Pump for a Specific Application?
Choosing the right size vacuum pump for a specific application involves considering several factors to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Required Vacuum Level: The first consideration is the desired vacuum level for your application. Different applications have varying vacuum level requirements, ranging from low vacuum to high vacuum or even ultra-high vacuum. Determine the specific vacuum level needed, such as microns of mercury (mmHg) or pascals (Pa), and choose a vacuum pump capable of achieving and maintaining that level.
2. Pumping Speed: The pumping speed, also known as the displacement or flow rate, is the volume of gas a vacuum pump can remove from a system per unit of time. It is typically expressed in liters per second (L/s) or cubic feet per minute (CFM). Consider the required pumping speed for your application, which depends on factors such as the volume of the system, the gas load, and the desired evacuation time.
3. Gas Load and Composition: The type and composition of the gas or vapor being pumped play a significant role in selecting the right vacuum pump. Different pumps have varying capabilities and compatibilities with specific gases. Some pumps may be suitable for pumping only non-reactive gases, while others can handle corrosive gases or vapors. Consider the gas load and its potential impact on the pump’s performance and materials of construction.
4. Backing Pump Requirements: In some applications, a vacuum pump may require a backing pump to reach and maintain the desired vacuum level. A backing pump provides a rough vacuum, which is then further processed by the primary vacuum pump. Consider whether your application requires a backing pump and ensure compatibility and proper sizing between the primary pump and the backing pump.
5. System Leakage: Evaluate the potential leakage in your system. If your system has significant leakage, you may need a vacuum pump with a higher pumping speed to compensate for the continuous influx of gas. Additionally, consider the impact of leakage on the required vacuum level and the pump’s ability to maintain it.
6. Power Requirements and Operating Cost: Consider the power requirements of the vacuum pump and ensure that your facility can provide the necessary electrical supply. Additionally, assess the operating cost, including energy consumption and maintenance requirements, to choose a pump that aligns with your budget and operational considerations.
7. Size and Space Constraints: Take into account the physical size of the vacuum pump and whether it can fit within the available space in your facility. Consider factors such as pump dimensions, weight, and the need for any additional accessories or support equipment.
8. Manufacturer’s Recommendations and Expert Advice: Consult the manufacturer’s specifications, guidelines, and recommendations for selecting the right pump for your specific application. Additionally, seek expert advice from vacuum pump specialists or engineers who can provide insights based on their experience and knowledge.
By considering these factors and evaluating the specific requirements of your application, you can select the right size vacuum pump that meets the desired vacuum level, pumping speed, gas compatibility, and other essential criteria. Choosing the appropriate vacuum pump ensures efficient operation, optimal performance, and longevity for your application.


editor by CX 2023-11-16